Loading
Journal of Cancer Immunology
ISSN: 2689-968X
2021
Volume 3, Issue 1, p1-65
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
TFAP-2: A Special Regulator with Bidirectional Effect in Human Cancer
Li-Nan Wang, Yi-Liu Yang, Lin-Yong Zhao
Abnormality of transcription factors’ activity has been found in signal pathways of many cancers. The AP-2 family of transcription factors (TFAP2) is one of the most representative families with this characteristic.
J Cancer Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 1, p1-5 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.3.035
Long Non-coding RNAs in the Pathophysiology of Multiple Myeloma New Insights on the Role of CRNDE
Simone Zocchi, Antoine David, Michele Goodhardt, David Garrick
Over the past 15 years, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNA) have emerged as an important class of regulatory molecules. The currently accepted definition is that lncRNA refers to RNA molecules with little or no protein-coding potential, and which are greater than 200 nucleotides in length, a size cut-off chosen largely to distinguish them from the more-extensively characterised group of small non-coding regulatory RNAs, which includes micro (mi)RNAs, small inhibitory (si)RNAs and PIWI-interacting (pi)RNAs.
J Cancer Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 1, p6-12 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.3.036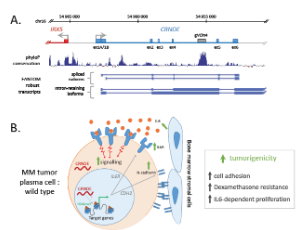
Small-molecule Interferon Inducers for Cancer Immunotherapy Targeting Non-T cell-inflamed Tumors
Eunha Kim, Sanghee Lee
Since the discovery of escaping mechanism of tumor from negative immune regulation, the paradigm of drug discovery for anti-cancer agents has been dramatically shifted to cancer immunotherapy (e.g., dendritic cell therapy, CAR-T cell therapy, or antibody therapy) by stimulating patient’s immune system to treat cancer.
J Cancer Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 1, p13-17 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.3.037
SHP2 Inhibition as a Promising Anti-cancer Therapy: Function in Tumor Cell Signaling and Immune Modulation
Jiawan Wang, Lindy Zhang, Christine A. Pratilas, Nicolas J. Llosa
The SHP2 phosphatase consists of one protein tyrosine phosphatase catalytic domain (PTP domain), two tandem Src homology 2 (SH2) domains (N-SH2 and C-SH2), and a C-terminal tail with two tyrosine phosphorylation sites (Tyr542 and Tyr580)
J Cancer Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 1, p18-29 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.3.038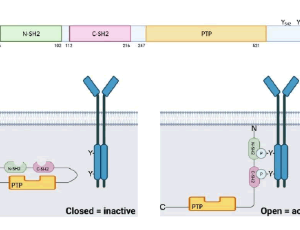
Expanding the Cancer Neoantigen Peptide Repertoire beyond In silico Tools
Amit Jain, Jackwee Lim
CD8+ cytotoxic T cells recognise and kill cancer cells that present immunogenic peptides bound to the cell surface major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) molecules.
J Cancer Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 1, p30-36 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.3.039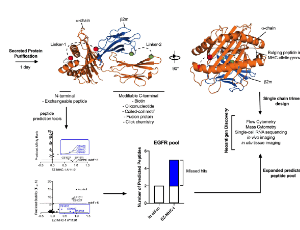
Lenalidomide Maintenance After Autologous Stem Cell Transplant: The Utility of Real-World Data and Future Areas of Study
Hannah M Cherniawsky, Christopher P Venner, Esther Masih-Khan, Donna Reece
Low-dose, lenalidomide maintenance following autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is the current standard of care in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM) based on results from large, randomized controlled trials and a meta-analysis which demonstrated improved overall (OS) and progressionfree survival (PFS).
J Cancer Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 1, p37-46 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.3.040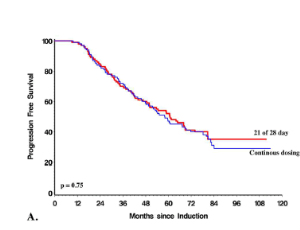
Immunogenic Cell Death: A Step Ahead of Autophagy in Cancer Therapy
Gourab Gupta, Kristina Borglum, Hexin Chen
Cell Death has long been considered to be an inevitable part of the life cycle of a cell and hence, considered a familiar consequence of cellular life.
J Cancer Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 1, p47-59 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.3.041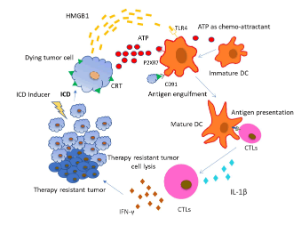
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Diagnosis, Therapy and Molecular Investigations
Veronica Bazzani, Riccardo Pravisani, Umberto Baccarani, Carlo Vascotto
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) accounts for approximately 90% of primary liver cancers and, with rapidly increasing incidence in the last two decades, constitutes a major global health problem.
J Cancer Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 1, p60-65 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.3.042
Recommended Articles
Constitutively Active Death Receptor Induces Apoptosis in Mammalian Cells
Apoptosis is a physiological response in development and homeostasis of metazoans. Apoptosis is triggered during pathological events as a means to renew affected tissues and eliminate cancer cells. The immune system regulates the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis, where signals such as TNFα or displayed ligands on the surface of immune cells trigger signal cascades by death receptors present on targeted cells.
Autophagy: When to strike?
Autophagy was originally viewed as a widely conserved multistep lysosomal degradation pathway in eukaryotes. It includes the formation of autophagosomes, doublemembrane structures engulfing cytoplasm with damaged organelles during the degradation process.
Immunogenic Cell Death: A Step Ahead of Autophagy in Cancer Therapy
Cell Death has long been considered to be an inevitable part of the life cycle of a cell and hence, considered a familiar consequence of cellular life.
A novel therapeutic strategy for antifibrotic based on a new gene NS5ATP9
By the suppression of subtractive hybridization (SSH) and yeast-two hybrid system, 127 new genes were screened, cloned, and registered at GenBank (Table 1) [1,2]. These new genes which were found in the liver have been demonstrated to be closely related to liver diseases such as viral hepatitis, liver fibrosis, fatty liver, and
Newly Identified Function of Caspase-6 in ZBP1-mediated Innate Immune Responses, NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation, PANoptosis, and Host Defense
Caspases are critical for regulating cell death, immune responses, and homeostasis. These cysteine-dependent endoproteases cleave their substrates after certain aspartic acid residues.
Commentary on “A Vaccine for Photodynamic Immunogenic Cell Death: Tumor Cell Caged b y Cellular Disulfide–Thiol Exchange for Immunotherapy”
Tumor immunotherapy, including monoclonal antibody of immune checkpoint blockade, therapeutic antibody, cancer vaccine and cell therapy, etc., is to restart and maintain the tumor immune cycle, restore the normal antitumor immune response of the body, so as to control and eliminate the tumor.
F-ATP Synthase Inhibitory Factor 1 in Regulation of Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore and Metabolic Reprogramming
Mitochondrial permeability transition pore (PTP) plays an important role in mitochondrial physiology and cell fate. Emerging studies highlight PTP forms from F-ATP synthase, but whether F-ATP synthase inhibitory factor 1 (IF1) regulates the activity of PTP is basically unknown. We have recently demonstrated that IF1 interacts with p53-CyPD complex and promotes opening of the PTP, and IF1 is necessary for the formation of p53-CyPD complex.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.