Loading
Journal of Nanotechnology and Nanomaterials
ISSN: 2692-630X
Latest Articles
Functionalized Carbon Nano-onions for Polymer Composites
Ahmad Adlie Shamsuri
Functionalized CNOs can be tailored through chemical modifications to enhance their compatibility with various polymer matrices, a practice that has seen increasing utilization across diverse fields. This editorial article examines the role of these functionalized nanoparticles in revolutionizing polymer composites, specifying briefly the techniques for their functionalization, the general types of polymer matrices used, their effects on composite properties, and their broadening range of applications.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.057
Cardiac Stents from Research to Clinical Applications
Shabnam Hashemzadeh , Saber Hashemzadeh , Fateme Bina
Early diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis are of vital importance in cardiology. Because of high risk and complexity of open-heart surgery, nowadays balloon angioplasty and stent implantation are common techniques to extend arterial vessels narrowed by atherosclerosis. Serious drawbacks of previous stents, such as complications induced by delayed healing and local hypersensitivity reactions and so re-narrowing and vascular reocclusion, have led to the development of stent designs, stent delivery systems, ultrasonic guidance of stent situation, and high-pressure dilatation post-stenting modifications [2-5].
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p4-11 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.058
Recent Advances in Different Nanoprecipitation Methods for Efficient Drug Loading and Controlled Release
A. W. Zaibudeen
Nanoprecipitation has emerged as a versatile and efficient technique for formulating nanoparticles, providing significant advantages in drug delivery applications. Nanomaterials, particularly polymer nanoparticles (PNPs), play a crucial role in encapsulating and controlling the release of drug molecules, serving as an alternative to traditional drug delivery methods. Various types and morphologies of PNPs have been synthesized using different nanoprecipitation methods that are being used as drug carriers, demonstrating superior performance in targeted drug delivery with controlled release compared to conventional methods.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p12-25 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.059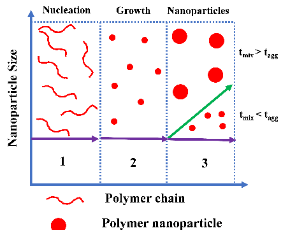
Comment on “Cholesterol Induced Asymmetry in DOPC Bilayers Probed by AFM Force Spectroscopy”
Dhruva Bhat , Appala Venkata Ramana Murthy
In the recent article, Adhyapak et al., used Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) and Force Spectroscopy to investigate the influence of cholesterol on the phase state behaviour of fluid phase DOPC membranes and found that the excess cholesterol conditions (above 20%) can induce an asymmetry in the lipid bilayer leading to changes both topography and more significantly in the nanomechanical properties of the lipid bilayer.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p26-27 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.060
Nanoscale Diagnosis and Therapy: Nanotheranostics as an Advance in Nanotechnology
Bianca Pizzorno Backx
The term "nanotechnology," introduced in 1986, refers to the emergence of a novel technology poised to transform existing protocols at the nanoscale. For many years, publications regarding nanotechnology have generated significant expectations related to discoveries and solutions. In 1990, with the inception of green chemistry, the scientific community began to reassess its approach, inspired by adaptations of protocols established by various eco-friendly institutions.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p28-42 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.061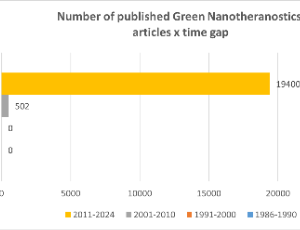
Cutting-Edge Nanoparticle Innovations in Biomedical Science: Synthesis, Applications, Challenges, and Future Prospects
Joicy John
Nanoparticles (NPs), identified as particles measuring between 1 and 100 nanometers, exhibit distinct physical and chemical properties that set them apart from larger materials. These attributes, which encompass a substantial surface area relative to volume and quantum phenomena, render them highly across various sectors.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p43-66 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.062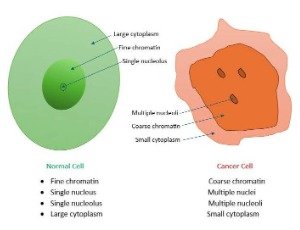
Development of Functional Nano-, Micro-Biostructures with Generation of New Enhanced Light Pathways for Life Science Applications
Daniela Alejandra Quinteros , M. Valeria Amé , A. Guillermo Bracamonte
Life sciences involve a broad overview of fundamental research of high interest, accompanied by the development of applications based on emerging needs. The generation of non-classical light is a high-impact area of research that could lay the foundation for functional materials, particularly in applications requiring tracking and switchable (on/off) properties. In this regard, the present communication is intended to present and discuss how natural and synthetic bio-structures, along with Nanotechnology, could provide versatile platforms for developing functional and multi-functional structures accompanied by the generation of novel non-classical light pathways.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p67-75 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.063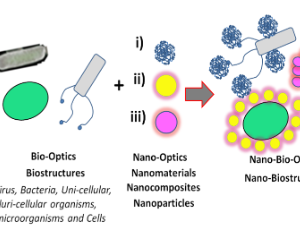
Weak Interactions in Catalysis
Xinyu Guo , Ziyang Feng , Bingyuan Zeng , TingTing Xia , Yuetong Zhao , Wenliang Zhang , Zumin Wang , Kun Zhao
Traditional catalytic theory has predominantly centered on static chemical bond processes, specifically the weakening, breaking, strengthening, and formation of chemical bonds – representing relatively fixed patterns of transformation. Whereas the dynamic regulatory mechanisms of weak interactions have been relatively understudied. This paradigm shift emerges from recognizing how precisely engineered 3D spatial arrangements govern catalytic efficiency: directional hydrogen bonds, size-matched hydrophobic cavities, and π-π stacking at optimal distances collectively create confined microreactors that steer reaction pathways.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p89-94 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.065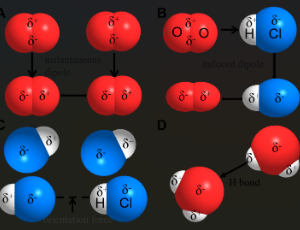
Enhancing p-type DSSC Performance through Nio-carbon Allotrope Hybrids: A Study of Functionalized MWCNT Integration
Nidhi Prajapati , Chivukula Narayana Murthy
In this study, we systematically investigated the influence of various carbon allotropes on the photovoltaic performance of p-type dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) using nickel oxide (NiO) nanotubes as the base semiconductor. The selected carbon nanostructures multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), reduced graphene oxide (RGO), graphene quantum dots (GQDs), and fullerenes (C60) were integrated with NiO and evaluated based on their structural and electrochemical characteristics.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p76-88 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.064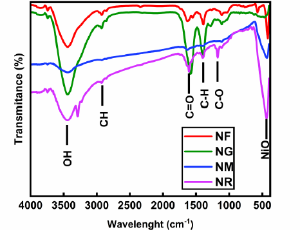
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
