Abstract
The quality of skin wound healing can be improved by the application of collagen scaffolds as biological dermal substitutes. Diacoll-SB Dermal Regeneration Template (SB-DRT) is an advanced bioengineered collagen-based matrix that serves as a promising solution in the management of burn injuries. This study investigates the efficacy and role of Diacoll-SB in burn treatment by examining its impact on wound healing, scar formation, and the need for skin grafting. This study highlights Diacoll-SB as a valuable adjunct in the management of burns, contributing to more effective and aesthetic healing of burn wounds.
Keywords
Diacoll-SB, Dermal regeneration template, Dermal extract, Collagen scaffold, Wound healing, Post burn raw area
Introduction
Burns are a common problem which accounts for a share of morbidity and mortality for every country. The management of post burns wounds pose a challenge and early wound healing can reduce morbidity to the patients, allowing a chance for early restoration back to their normal life. Continuous research has led to advancements in burn wound care to allow for early wound healing and better functional recovery [1]. Conventional treatments for burn wounds often include debridement and skin grafting, which are resource-intensive and not without complications. The need for alternative solutions has led to the development of bioengineered materials like Diacoll-SB Dermal Regeneration Template. Diacoll-SB is a collagen-based matrix designed to support dermal regeneration, enhance wound healing, and reduce scar formation. Dermal substitute is defined as biomatrices which fulfil the function of cutaneous dermal layer and provides matrices and scaffold for new tissue growth and thus increases the rate of wound healing [2]. The collagen-GAG scaffold helps in supporting the in-growth of connective-tissue cells, thus causing regeneration of tissue providing the critical physiological functions of dermis [3].
The purpose of this study is to evaluate Diacoll-SB's efficacy in the management of burns, comparing it to traditional burn care treatments and highlighting its potential to improve clinical outcomes in burn patients.
Case Report
A 42 years old female presented to the tertiary care burn centre with a history of accidental scald burns due to hot water 5 days back. Patient had mixed second-and third- degree scald burns over her abdomen, left ankle and right thigh with approximately 5% body surface area as per Lund and Browder Chart. On admission, patient was managed as per ATLS guidelines. Adequate analgesia and fluid resuscitation as per Parklands formula were started. A collagen dressing was done on admission which was repeated every day. POD-3 revealed most of the post burn wounds healed well except for 3% post burn raw area over left ankle, abdomen and right thigh. Patient was operated for Hydrojet debridement of slough with regenerative wound therapy with sucralfate. Regenerative collagen scaffold Diacoll – SB (Figure 1) dressing was done on POD-10 under LA (Figure 2). Upon removing the dressings on POD10 revealed most of the post burn wounds healed well. A collagen dressing was removed and the wounds had healed completely on POD 11. Patient was advised for 1 month with post burn scar management in the form of compression garments, coconut oil massage, silicone gel and sunscreen application. All wounds healed well without hypertrophic scar formation or wound breakdown on follow up upto 1 month.
Figure 1. Diacoll – SB
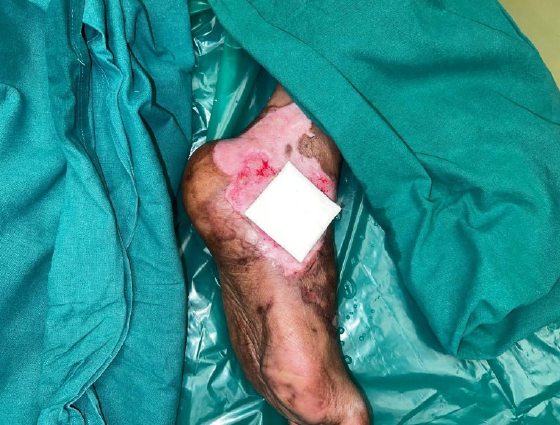
Figure 2. Dressing performed on postoperative day 10 over the left ankle.
Discussion
Yannas and Burke in their landmark study on basic requirements of artificial dermal substitutes highlighted its use in wound healing [4]. Various available dermal substitutes are like collagen scaffolds, synthetic materials, or cadaveric skin [4]. In burn patients, the available donor sites are limited. Split thickness graft usually is associated with donor site morbidity and may provide poor cosmetic outcome [5]. An ideal dermal substitute should be inexpensive, have a long life, can be used off the shelf, analgesic, durable, flexible, non-antigenic, prevents water loss, conforms to irregular wounds, and microbial, and can be used in a single sitting [6]. Collagen is well known for its advantages such as easy to remove, inexpensive, pain free, hypoallergenic, various sizes, ability to store for 3 years and ability to incorporate drugs and growth factors which are released in a controlled manner [7]. Dermal extract is known to augment wound healing with improved granulation and formation of epithelial islands promoting faster epithelisation [8]. The procedure can be performed under local anaesthesia with primary closure of the donor site and hence minimal donor site morbidity. Since the tissue is autologous, it doesn’t leads to antigenic reaction. Thus by combining collagen scaffold and dermal extract, the wound healing can be augmented in patients, providing faster wound healing. The findings of this study support the hypothesis that Diacoll-SB Dermal Regeneration Template enhances burn wound healing, reduces the need for skin grafting, and minimizes scarring. The collagen matrix in Diacoll-SB provides a scaffold for cellular infiltration and extracellular matrix deposition, crucial for the regeneration of dermal tissue. The shorter healing times observed in the treatment group may be due to this enhanced regenerative process. The reduced incidence of hypertrophic scarring in the Diacoll-SB group could be attributed to its ability to modulate the healing environment, preventing excessive collagen deposition. Additionally, the reduction in infection rates and pain levels can be explained by the moist wound healing environment maintained by Diacoll-SB, which promotes optimal conditions for healing while minimizing microbial growth. While these results are promising, there are limitations to the study, including its sample size and the short follow-up period. Further research with a larger cohort and extended follow-up is needed to assess the long-term effectiveness and safety of Diacoll-SB.
Conclusion
Diacoll-SB Dermal Regeneration Template is an effective therapeutic option in the management of burn injuries. It significantly accelerates wound healing, reduces the need for skin grafting, and minimizes the occurrence of hypertrophic scarring. Diacoll-SB offers a promising alternative to traditional treatments, improving both functional and aesthetic outcomes for burn patients. As a cost-effective, easy-to-apply solution, it has the potential to revolutionize burn care, particularly in resource-limited settings.
References
2. Shahrokhi S, Arno A, Jeschke MG. The use of dermal substitutes in burn surgery: acute phase. Wound Repair Regen. 2014 Jan-Feb;22(1):14-22.
3. Divya Sree D, Saranya D. Artificial skin scaffold to treat burn scars and its other applications. IJPBS 2015 Apr-Jun;5(2):11-24.
4. Yannas IV, Burke JF. Design of an artificial skin. I. Basic design principles. J Biomed Mater Res. 1980 Jan;14(1):65-81.
5. Ryssel H, Gazyakan E, Germann G, Ohlbauer M. The use of MatriDerm in early excision and simultaneous autologous skin grafting in burns--a pilot study. Burns. 2008 Feb;34(1):93-7.
6. Lineen E, Namias N. Biologic dressing in burns. J Craniofac Surg. 2008 Jul;19(4):923-8.
7. Mathangi Ramakrishnan K, Babu M, Mathivanan, Jayaraman V, Shankar J. Advantages of collagen based biological dressings in the management of superficial and superficial partial thickness burns in children. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2013 Jun 30;26(2):98-104.
8. Babu P, Chittoria RK, Pandey S, Bibilash BS et al. Collagen and dermal extract scaffold: A novel cover for burn wounds following tangential excision. Dermatology International. 2016 dec;1(2):69-72.