Loading
Journal of Cellular Signaling
ISSN: 2692-0638
2023
Volume 4, Issue 2, p49-92
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Potential Mechanism of CDC42 Promoting HCC Metastasis
Miaoling Tang, Rongni Feng, Jun Li
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an aggressive malignancy with increasing morbidity and mortality worldwide. The migration and motility of HCC tumor cells are enhanced by the formation of invadopodia, which comprise membrane protrusions at the leading edge. Previous studies have showed that cell division cycle 42 (CDC42) plays an essential role in remodeling the cytoskeleton, which is associated with invadopodia formation and thus mediates cellular movement.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p49-55 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.091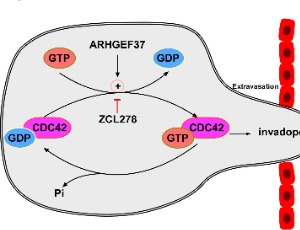
Novel Drug Development for Treatment of COVID-19 by In Silico Analysis: Identification of SARS-Cov-2 Inhibiting Streptomyces Compounds
Jayant Kumar, Prachiti Gholap, Thulasi G Pillai
In accordance with the present epidemiological paradigm, viral mutations of the virus are on the rise, and their natural effects are being selected for at a higher rate than normal. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the global COVID-19 pandemic induced by the Delta and Omicron strain of the SARS-CoV-2 virus could propagate and disseminate more rapidly than other viruses thanks to its many mutations, and these also caused some very significant health problems.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p56-72 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.092
A Study on the Usage of Probiotics as a Safer Antipyretic
Shantanu Shrivastava, Nimisha Bhatu
Most medicines and supplements which include probiotics have both expected clinical outcomes and unwanted side effects, which plays a major role when considering them as a mode of treatment. This review is an update about the advantages and disadvantages associated with the use of probiotics as part of a safe therapeutic armamentarium in health and other diseases. The advantages of probiotics run across multiple tissue systems in the body and a has a wide age spectrum.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p73-77 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.093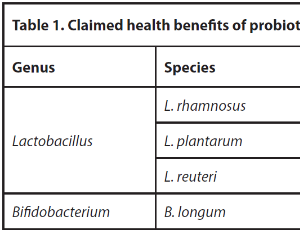
Understanding Chromosome Replication and Segregation Unit of Mycobacterium and Its Comparative Analysis with Model Organisms: From Drug Targets to Drug Identification
Preeti Jain
Bacterium maintains its pathogenicity in the host by continuing replication and adopting temporal and spatial coordination of cell division steps such as cell wall synthesis, DNA replication, chromosome segregation, Z ring assembly, septum formation and finally cytokinesis. This multistep process requires spatiotemporal assembly of macromolecular complexes and is probably regulated by redundant and multifunctional activities of cell replication and division proteins.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p78-85 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.094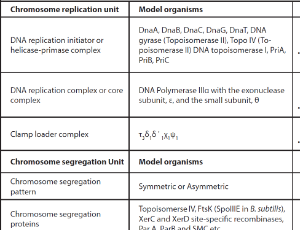
Improving Cancer Epigenetic Therapy; A Glimpse of NRF2
Tahereh Kashkoulinejad-Kouhi
One of the mechanisms used by epigenetic therapy is the elevation of host cell-derived double stranded RNA (dsRNA) baseline levels through overexpression of genomic repetitive elements especially Alu retroelements. The dsRNAs trigger immunogenic responses since immune system cannot distinguish between endogenous and exogenous dsRNAs derived from viral infections; hence called “Viral mimicry response”. These dsRNAs are recognized by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) such as MDA-5
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p86-92 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.095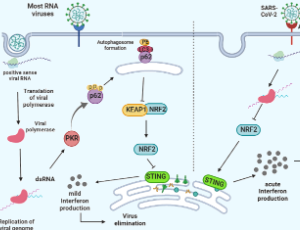
Recommended Articles
Deubiquitinase as Potential Targets for Cancer Immunotherapy
During the last few decades, immunotherapy is considered to be an important approach to help our immune system to fight various kinds of diseases, such as tumor. Sometimes, it works very well for some types of cancers, for example: bladder cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer and lymphoma.
The Potential Role of SEPT6 in Liver Fibrosis and Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Liver fibrosis is a reversible wound-healing response in which a variety of cells and factors are involved in and results in excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM). Cirrhosis is one of the significant causes of portal hypertension and end-stage liver disease, and it is the 14th most common cause of death around the world. Approximately 1.03 million people worldwide die from liver cirrhosis every year.
Prognostic Utility of Ferritin Transferrin Ratio in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
There is growing body of literature to identify novel prognostic markers in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), including serum ferritin (SF), transferrin levels, alfa fetoprotein (AFP), and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR). Chronic inflammation and fibrogenesis are considered quite essential in the oncogenesis of HCC. The trigger for this inflammation could range from viral hepatitis, alcoholic cirrhosis, to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Also, iron overload as in hereditary hemochromatosis is linked to one of the factors for HCC oncogenesis.
Prognosis and Survival of Medullary Carcinoma of the Breast
Medullary breast carcinoma (MBC) is a rare tumor, representing 3% to 5% of invasive breast carcinomas. The World Health Organization defines it as a well-circumscribed invasive tumor, composed of poorly differentiated cells, arranged in sheets, without gland formation and a scarce collagen stroma with the presence of a very prominent lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate.
Acute Abdomen due to Perforation of Small Bowel Malignant Melanoma Metastasis
Primary tumors of the small bowel are a rare condition, accounting for 2 to 3% of gastrointestinal tumors. Malignant melanoma is the most common metastatic tumor found in the gastrointestinal tract [1]. It can be localized in different sites, from the oral cavity to the anus. It can also be present as a primary lesion.
Radical Radiotherapy of Locally Advanced Cervix Uteri Carcinoma
Cervix uteri carcinoma is the most common gynecological cancer worldwide. In addition, it is the fourth most common malignancy and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death in women [1]. The most common histopathological subtype is squamous cell carcinoma (85%).
In silico Analysis for the Repurposing of Broad-spectrum Antiviral Drugs against Multiple Targets from SARS-CoV-2: A Molecular Docking and ADMET Approach
SARS-CoV-2 belongs to the genus Beta of the Coronaviridae family of enveloped single-stranded, positive-sense ribonucleic acid (RNA) with a genome length of 30,000bp. The virion is composed of various non-structural (RNA dependent RNA polymerase also known as RdRp) and structural proteins such as Spike (S), Nucleocapsid (N), Matrix (M), and Envelope (E) proteins.
Primary Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of Bladder – A Rare Diagnostic Entity
Primary small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the urinary bladder is a rare histological type shows poor differentiation and behaves in a highly aggressive manner. It accounts to 0.3- 0.7% of all bladder tumors [1,2]. Neuroendocrine carcinomas predominantly occur in respiratory and gastrointestinal tract and very rarely in the urinary bladder.
Dexamethasone: The First Drug to be Shown to Decrease Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19
The precise role of corticosteroids for treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is unclear due to lack of randomized trials.
How to Prevent Rehospitalization in Patients with COVID-19
Since December 2019, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) caused by 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) has resulted in 89,000 cases of Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), formerly known as Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (NCP) in China, including 2,450 deaths.
Leucocyte-Tumor Cell Hybridization Can Initiate Cancer Metastasis
According to estimates from the International Agency for Research on Cancer, by the year 2030 there will be 22 million new cancer cases and 13 million deaths per year. The main reason for death from cancer is not the initial tumor but it’s metastasis to distant parts of the body, yet this process has remained poorly understood for quite some time.
CTLA-4 and PD-L1 or PD-1 Pathways: Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Cancer Immunotherapy
The immune system developed certain checks and balance to control or inhibit the reactivity against normal cells of the body. Uncontrolled immune responses to the non-self entities such as bacteria, viruses, parasites, or mutated self-antigens can cause an inflammatory reaction and autoimmune diseases.
Cancer Nanomedicine: Strategies to Enhance Tumor Delivery and Immunotherapy
Cancer nanomedicine was originally developed for more efficient delivery of chemotherapeutic agents into tumor, and has been extensively employed as a therapeutic for cancer treatment owing to its unique features in drug delivery, diagnosis and imaging, as well as the therapeutic nature of some nanomaterials themselves.
Preparing for a More Public Health-Aware Practice of Medicine in Response to COVID-19
After one year in a pandemic, we mourn the loss of over half a million lives in the United States, and over four million worldwide, and remain concerned over the challenges facing the families of 35 million people in the United States, and 200 million worldwide, who have suffered from cases of COVID-19.
Targeting "Do Not Eat Me" Signal CD47 in Cancer Immunotherapy
Cells of the innate and adaptive arm of the immune system including macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells, neutrophils, T cells, and B cells, etc. are crucial for the maintenance of the body’s homeostatic balance and prevention of multiple diseases including cancer.
Aerosol Distribution Pattern of a Single-port Device: New Perspective Treatment for Peritoneal Carcinomatosis in Brazil
The local and peritoneal recurrence play a vital role in the natural history of the evolution of gastrointestinal and ovarian neoplasms. Different methods of applying intraperitoneal chemotherapy were used perioperatively to consolidate or control peritoneal carcinomatosis.
Verrucous Carcinoma of the Esophagus: Its Unique Etiology and Association with Human Papilloma Virus
Verrucous carcinoma is an extremely rare disease, and it is unique in terms of its appearance, growth pattern, and etiology. In 1948, Ackerman first described verrucous squamous cell carcinoma (VSC) as a variant of oral squamous cell carcinoma, and he collected 31 cases of oral neoplasms under the name, “Verrucous Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity.”
Are We Close to Achieving a HBV Cure? Risk for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Persists Despite Long-term HBV Suppression: An Update on Our Experience
Since the discovery of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) by Blumberg et al., great progress has been made in understanding the pathogenesis of the virus and its role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). It is estimated that hepatitis B is responsible for about 50% of the HCC cases worldwide. Because of geographic variations in HBV incidence, the burden of HBV-related HCC (HBV-HCC) is highest in endemic areas such as Asian-Pacific and sub- Saharan Africa and lowest in the United States and the West. The hepatitis B vaccines, developed in the 1980s, transformed the evolution of hepatitis B in the modern era. This was followed by high effective anti-viral that reduced HBV infections and HBV-HCC.
Involvement of D-Loop Mutations in the Occurrence of Ovarian Carcinoma
Each cell in the body contains hundreds of mitochondria; each mitochondrion contains several DNA molecules, each carrying 37 genes that participate in the production of energy.
Fatty Liver and Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Fatty liver (FL) is the most common wide-world liver disease that is nowadays demonstrating an increasing prevalence trend. In sharp contrast, the most common causes of liver diseases, such as viral causes, are decreasing thanks to advances in antiviral therapies. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is characterized by hepatic fat accumulation, often associated with insulin resistance (IR), and defined by the presence of steatosis in at least 5% of hepatocytes in absence of relevant alcohol intake.
Trending Special Issues
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.