Loading
Archives of Medical Case Reports
ISSN: 2691-7971
2020
Volume 2, Issue 1, p1-35
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Healthy Fetal Outcomes Using A Novel Treatment For Maternal Lyme Disease And Babesiosis During Consecutive Pregnancies: A Case Study and Literature Review
Richard Horowitz, Phyllis R. Freeman
The genus Babesia comprises over 100 species of tick-transmitted protozoal intraerythrocytic pathogens (piroplasms) [1], causing malarial-type illness. The most common human pathogens in the United States are B. microti [2] and Babesia duncani (WA- 1) [3]; Less common species include Babesia MO-1 [4] and KO-1 [5], as well as Babesia divergens and Babesia venatorum (EU-1) in Europe.
Arch Med Case Rep, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 1, p1-19 | DOI: 10.33696/casereports.2.006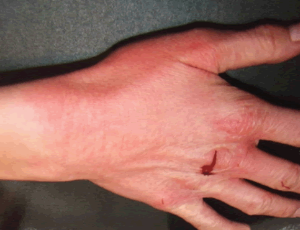
Role of Topical Insulin in Venous Ulcer Management
Neljo Thomas, Ravi Kumar Chittoria, Saurabh Gupta, Chirra Likhitha Reddy, Padmalakshmi Bharathi Mohan, Shijina K, Imran Pathan, Nishad K
Wound healing is a dynamic process whereby cellular structures and the tissue layers are reconstructed. Adult wound healing can be categorized into three stages: inflammatory phase, proliferative phase, and remodelling phase. Blood cells like macrophages, neutrophils, extracellular matrix and mediators, various proteins, and various genes play an important role in these phases.
Arch Med Case Rep, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 1, p20-22 | DOI: 10.33696/casereports.2.007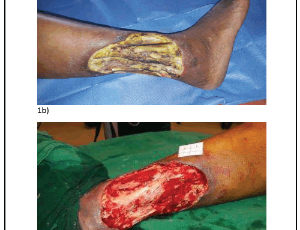
Safety and Efficacy of s-MOX Regimen in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Who Developed Cardiotoxicity Following Fluoropyrimidine Administration: A Case Series
Matthew I. Ehrlich, Kristin Kaley, Melissa Smith, Muhammad Wasif Saif
5-fluorouracil (5-FU), an antimetabolite in the fluoropyrimidine class, is the third most commonly used chemotherapeutic agent worldwide for the treatment of solid malignancies [1]. Despite advances in novel cancer therapies, commonly used in combination with fluoropyrimidines, 5-FU remains one of the most effective and safe chemotherapy agents to manage colorectal cancer (CRC).
Arch Med Case Rep, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 1, p23-29 | DOI: 10.33696/casereports.2.008
Double Trigger, Reverse Triggering, and Pseudo-Reverse-Triggering
José Antonio Benítez Lozano, José Manuel Serrano Simón
The double trigger (DT) is the second asynchrony in frequency, after the failed cycles [1]. Compared to the latter, it can be more injurious since it usually increases tidal volume (Vt), transmural and transvascular pressure to levels that can cause ventilator-induced lung damage [2,3]; and self-inflicted by the patient (P_SILI) [4], as well diaphragmatic injury.
Arch Med Case Rep, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 1, p30-35 | DOI: 10.33696/casereports.2.009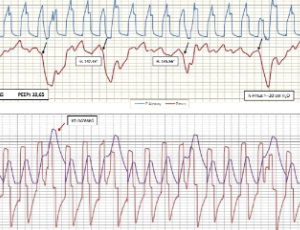
Recommended Articles
Safety and Efficacy of s-MOX Regimen in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Who Developed Cardiotoxicity Following Fluoropyrimidine Administration: A Case Series
5-fluorouracil (5-FU), an antimetabolite in the fluoropyrimidine class, is the third most commonly used chemotherapeutic agent worldwide for the treatment of solid malignancies [1]. Despite advances in novel cancer therapies, commonly used in combination with fluoropyrimidines, 5-FU remains one of the most effective and safe chemotherapy agents to manage colorectal cancer (CRC).
Insights of CECCY Trial: Should Troponin be the Target for Anthracycline Cardiotoxicity Prevention?
Advances in oncology such as better access to health care system, earlier cancer diagnosis and new chemotherapies have led to longer survival of oncologic patients over the last decades. However, this population is vulnerable to cardiovascular drug-related adverse events like cardiomyopathy, which leads to heart failure and impairs survival and quality of life.
Progress in Diagnosis and Treatment of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated Cardiotoxicity
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are a new type of broad-spectrum antitumor drugs, which mainly include cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein-4 (CTLA-4) inhibitors, programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) and its ligand PD-L1 inhibitors. Since 2011, ICIs have been approved for more than 20 kinds of malignant tumors.
High Throughput Image Analysis for Cardiotoxicity Study using Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes
Severe cardiotoxic side-effects are found in patients who are treated with anti-cancer drugs from both earliest chemotherapeutics (for example anthracyclines, such as Doxorubicin) and novel therapeutic compounds, such as monoclonal antibodies and small molecules inhibiting tyrosine kinases; e.g. crizotinib.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
