Loading
International Journal of Anesthesia and Critical Care
ISSN: 2834-2887
Featured Articles
Gender Disparities in Outcomes Following Pulmonary Embolism Treatment in the Intensive Care Unit; A Multi-center Retrospective Cohort Study
Reubeni E. Mkama, Jin Peng, Yan Zhou, Tingfa Zhou, Jinyun Du, Guozhong Pang, Min Si, Yuan Li, Weidong Qin, Xiaomei Chen
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of blood flow in the pulmonary artery bed that can result in a life-threatening and potentially reversible right ventricular failure [1]. PE remains one of the leading causes of poor prognosis and death, particularly when a shock or right ventricular failure occurs [2]. According to studies, PE is generally manifested in a nonspecific manner
Int J Anaesth Crit Care, 2022, Volume 1, Issue 1, p5-16 | DOI: 10.33696/Anesthesia.1.002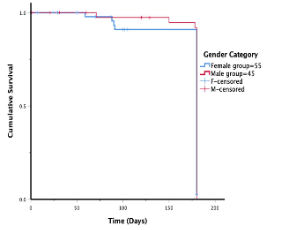
Acute and Chronic Pain Management of the Urologic Patient
Jonathan Varghese, David L. Chang, Benjamin D. Mirman, Jillian Capodice, Mourad Shehebar
Objectives: Here, we review opioid-sparing or opioid-free anesthesia and pain management for urologic procedures and pathologies–urological pain syndromes, kidney stone pain management, development of post-surgical pain syndromes, and prevention. We explore acute management of perioperative pain during and after urologic procedures; additionally, we review the pathophysiology of various urologic pain syndromes along with a variety of interventions, including pharmacologic management, nerve blocks, neurolysis, and neuromodulatory therapies in hopes of educating providers who treat the urologic patient.
Int J Anaesth Crit Care, 2024, Volume 3, Issue 1, p6-16 | DOI: 10.33696/Anesthesia.3.008
Evolving Policies and Practices for Organ Recovery and Non- Lung Organ Transplantation in Candidates Recovering from COVID-2019 - A Review
Yehuda Raveh, Rodrigo Vianna, Alghidak Salama, Ramona Nicolau-Raducu
The Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic affected Solid-Organ transplantation (SOT) policies and practices worldwide. The medical sector had to adapt to overwhelming concerns regarding patient care, infection-control, healthcare workers’ safety, and limited healthcare resources. Transplant-
Int J Anaesth Crit Care, 2022, Volume 1, Issue 1, p17-23 | DOI: 10.33696/Anesthesia.1.003
The Impact of Fluid Resuscitation Timeliness in Geriatric Patients with Sepsis: A Single Center Retrospective Cohort Study
Zed Omar Seedat, Kevin Itty, Prashank S. Neupane, Katherine D. Reano, David L. Waldburg, , Christopher M. Gebara, Samer Fahmy, Michael A. DeDonno, Sachin S. Sule
Sepsis is a key driver of worldwide mortality, representing close to 20% of global deaths in 2017 [1]. Approximately half of patients hospitalized with sepsis are 65 years and older [2]. Delivery of 30ml/kg of crystalloid fluid bolus within three hours of diagnosing sepsis remains a cornerstone of the Surviving Sepsis Campaign (SSC)
Int J Anaesth Crit Care, 2022, Volume 1, Issue 1, p24-32 | DOI: 10.33696/Anesthesia.1.004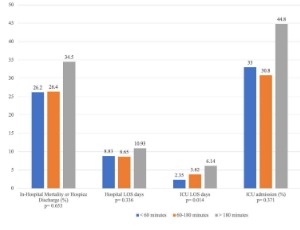
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
