Loading
Journal of Experimental Neurology
ISSN: 2692-2819
2024
Volume 5, Issue 1, p1-41
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
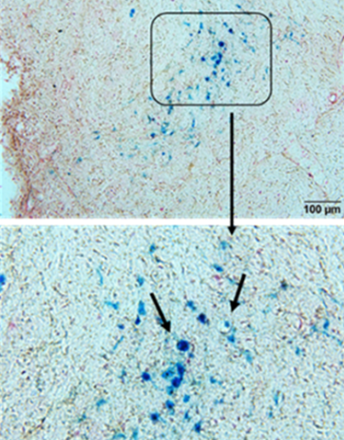
CCR3 Expression in Relation to Delayed Microbleeds in a Rat Model of Large Vessel Occlusion
Sydney M Claypoole, Jacqueline A. Frank, Sarah J Messmer, Keith Pennypacker
Thirty percent of ischemic stroke patients develop vascular cognitive impairment and dementia (VCID) within 1 year of stroke onset. The expression of C-C motif chemokine receptor 3 (CCR3) is associated with endothelial dysfunction and memory impairment. CCR3 has been reported to increase after experimental stroke and in human stroke patients. Using an in vivo model of stroke, our study aims to link CCR3 expression with endothelial dysfunction in this rodent stroke model.
J Exp Neurol, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 1, p1-8 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.5.082
Could Neonatal Electroclinical Syndromes Orchestrate Diagnosis and Treatment?
Rene Andrade Machado
Neonatal seizures are associated with neurodevelopmental impairments. Implementing long-term video-EEG monitoring in the neonatal intensive care unit became the gold standard for seizure diagnosis. During the neonatal period, seizures can be associated with an acute brain insult called acute symptomatic seizures (ASS) or being part of neonatal epilepsy that may have a structural, metabolic, or genetic cause.
J Exp Neurol, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 1, p9-18 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.5.083
Mechanical Thrombectomy for All LVO – Is It Feasible? – Recent Evidence to Expand the Current Stroke Guidelines
Jindong Xu, Cortney de La Torre, Devon Shafer, Margely Carrion-Carrero, Pramod Sethi
Mechanical thrombectomy (MT) has established its role as a standard care of acute ischemic stroke due to large vessel occlusion (LVO). Current early stroke management guidelines have defined certain selection criteria for LVO patients undergoing MT to achieve the most benefit. However, it is still uncertain if some other LVO patients who do not meet these criteria can also benefit from MT.
J Exp Neurol, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 1, p19-34 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.5.084
Diagnosis and Treatment of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus and Repeated Subdural Hematoma and Effusion after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt in the Elderly: A Case Report
Qing-Yong Wang, Qingjun Li
Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) is a special type of hydrocephalus that is characterized by cognitive decline, gait disturbance, and urinary incontinence. It can lead to dementia and bedridden within 1-3 years. Without surgical treatment in time, the prognosis was bleak. We report an iNPH case misdiagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease, with a disease course of 3 years.
J Exp Neurol, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 1, p35-39 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.5.085
Definition and Characteristics of Multiple Sclerosis with Predominant Cognitive Presentation
Amanda Fiori Cavassani, Álix Djone Berté, Andressa Ribeiro Pinto, Marcus Vinicius Magno Gonçalves, Gabriel de Deus Vieira
We recently reported a longitudinal MRI and cognitive follow-up of a patient with multiple sclerosis with predominant cognitive presentation (MSCP), showing the evolution of the disease and the difficulty in its early diagnosis [1]. In this commentary, we will briefly overview the definition and clinical manifestations of MSCP.
J Exp Neurol, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 1, p40-41 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.5.086
Recommended Articles
The Endothelium: Global Integrator of Vascular-Immune Interactions
Endothelial cells (ECs) are mesodermally-derived modified simple squamous epithelial cells that collectively form the vascular endothelium–the vast living shield that lines the luminal surface of all blood vessels, the lymphatic circuit, and heart. Endothelial cell phenotypes vary among different organs and tissues with regard to specific barrier characteristics, and can be altered by environmental stimuli
Dendorbium Nobile Lindl. Alkaloids Suppress NF-κB and NLRP3 Signaling Pathways to Attenuate Lipopolysaccharide-induced Neuroinflammation
The important immune cells in the brain are called microglia acting as the central junction between neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. In patients of cognitive disorders and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) animal models, amoebic morphology and inflammatory pathways are activated to release numerous cells in the inflammatory factors by active microglia.
EMG Signal Processing for Hand Motion Pattern Recognition Using Machine Learning Algorithms
Stroke is a major cause of death and disability in the world. There were approximately 25.7 million stroke survivors and 6.5 million deaths from stroke [1]. Stroke can result in arm disability and reduce daily life activity via weak arm muscle activity [2]. Studies have been performed to discover therapeutic and assistive approaches to compensate for disabilities and restore functions.
Negative is Not Always Negative: Improving Outcomes in Scalp Negative Seizures Using Intracranial EEG
Refractory seizures sometimes arise from deeper foci within the brain. When difficult to detect on scalp EEG, chances of successful epilepsy surgery are reduced. Two patients had scalp Electroencephalogram (EEG) negative seizures, got intracranial EEG and did well with responsive nerve stimulation (RNS).
Much is Known about Caregiver Burden in Dementia - What is Next? The Role of Comorb idities and Future Perspectives
Care for patients with chronic debilitating neurological diseases is often demanding and can result in a variety of negative consequences including mental and physical morbidity.
SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The Viral Arms Race and Pattern- Recognition Receptors
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARSCoV-2), the causative agent of COVID-19 respiratory disease, was first identified on 7 December 2019, and quickly spread worldwide. The SARS-CoV-2 belongs to Coronaviridea family, enveloped single-stranded RNA viruses. The family is divided into two subfamilies, the Coronavirinae and the Torovirinae, distinguished by the shape of their nucleocapsids . Virions are roughly spherical and are notable for the large spike (S) glycoprotein that mediate viral entry to the host cell. The subfamily Coronavirinae consists of four genera, the alpha-, beta-, gamma-, and delta-coronaviruses. There are seven coronaviruses that can infect people – four of them causing a common cold (229E, NL63, OC43, HKU1), and three are associated with potentially severe respiratory conditions, namely severe syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), and the emerging type of SARS-CoV-2, which has 79% sequence homology with SARS-CoV.
The Use of CHA2DS2-VASc Score to Predict Functional Outcomes of Mechanical Thrombectomy
Background: Mechanical thrombectomy is widely used for revascularization of acute ischemic strokes from large vessel occlusions. Functional outcomes following mechanical thrombectomy are typically assessed using the modified Rankin scale. CHA2DS2-VASc score is commonly used to estimate the stroke risk of patients with atrial fibrillation, but studies have verified its use in other various situations. Our study aimed to assess the utility of CHA2DS2-VASc score in predicting outcomes of patients undergoing mechanical thrombectomy.
CCR3 Expression in Relation to Delayed Microbleeds in a Rat Model of Large Vessel Occlusion
Thirty percent of ischemic stroke patients develop vascular cognitive impairment and dementia (VCID) within 1 year of stroke onset. The expression of C-C motif chemokine receptor 3 (CCR3) is associated with endothelial dysfunction and memory impairment. CCR3 has been reported to increase after experimental stroke and in human stroke patients. Using an in vivo model of stroke, our study aims to link CCR3 expression with endothelial dysfunction in this rodent stroke model.
Mechanical Thrombectomy for All LVO – Is It Feasible? – Recent Evidence to Expand the Current Stroke Guidelines
Mechanical thrombectomy (MT) has established its role as a standard care of acute ischemic stroke due to large vessel occlusion (LVO). Current early stroke management guidelines have defined certain selection criteria for LVO patients undergoing MT to achieve the most benefit. However, it is still uncertain if some other LVO patients who do not meet these criteria can also benefit from MT.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus and Repeated Subdural Hematoma and Effusion after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt in the Elderly: A Case Report
Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) is a special type of hydrocephalus that is characterized by cognitive decline, gait disturbance, and urinary incontinence. It can lead to dementia and bedridden within 1-3 years. Without surgical treatment in time, the prognosis was bleak. We report an iNPH case misdiagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease, with a disease course of 3 years.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
