Loading
The Archives of Psychiatry
ISSN: 2995-8776

2023
Volume 1, Issue 1, p1-50
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
The Future of Jail-Based Competency Treatment: Commentary from 30,000 Feet
Jerry L. Jennings, Kevin Rice
In their recent article, “Jail-Based Competency Treatment Comes of Age,” Jennings et al. [1] reviewed the historical development of the model and presented the first large-scale empirical support for its effectiveness, which covered eight years of outcomes across four different program sites for nearly 2,000 Incompetent to Stand Trial (IST) defendants.
Arch Psychiatry, 2023, Volume 1, Issue 1, p1-6 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.1.001
Suicide and Violent Behavior in Psychotic Inpatients
Jayatamarai Vijayen, Koh Ong Hui, Amer Siddiq
This study compares the association between psychosis, suicide, and violent behavior in patients admitted and discharged from the psychiatric ward. Methods: This study used a cross-sectional design. The experimental study was done with all the psychotic patients fulfilling the inclusion criteria upon admission and discharge from a teaching hospital in Malaysia. The study was conducted for a duration of five months from March to July 2022.
Arch Psychiatry, 2023, Volume 1, Issue 1, p7-13 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.1.002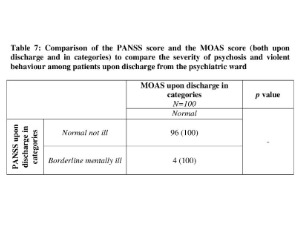
Clinical Characteristics of Outpatient Adolescents Undergoing Ongoing Psychotherapy in a Greek Tertiary Hospital from June 2016 to December 2019
Voultsos P, Tsamadou E, Demertzi E
Background: Adolescents with mental disorders often have difficulty engaging in ongoing treatment. Dropout from treatment is common. Aim: This paper aims to explore the clinical characteristics of a cohort of adolescents with mental disorders who were stably and actively undergoing psychotherapy over a relatively long period of time (for at least four months).
Arch Psychiatry, 2023, Volume 1, Issue 1, p15-28 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.1.003
Self-Reliance Therapy: Reflections and a New Model
Amaresh Nath, Harish Bhuvan
Background: Using the learnings and reflections from their professional and personal journeys, the authors believe that every “Neurosisoriented” mental health concern has four root causes: self-love (a lack of it), fear, grief, and aim (a lack of it). Using this as the premise, the authors have developed a new therapeutic modality that incorporates 12 primary universal formulas that they have conceptualized.
Arch Psychiatry, 2023, Volume 1, Issue 1, p29-38 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.1.004
Alexithymia in Alcohol Dependence – A Case Control Study from a Rural Tertiary Health Care Centre
Harshal Shriram Sathe, Shraddha Borhade, Aishwarya Awalekar, Janhavi Purandare, Sagar Karia
Background: Alexithymia is a personality trait characterized by difficulty in identifying, expressing, and describing one’s emotions. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the relationship between alexithymia and alcohol dependence. Several studies have found that alexithymia is more prevalent in individuals with alcohol dependence compared to healthy controls.
Arch Psychiatry, 2023, Volume 1, Issue 1, p39-44 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.1.005
The Role of Patient-Reported Social Factors in Promoting Buprenorphine Consistency
Brenna Cook, Michelle Eglovitch, Dace Svikis, Caitlin E Martin
Background: While medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD) reduce overdose risk, inconsistent use can lead to substance use recurrence and compromise achieving optimal opioid use disorder (OUD) treatment outcomes. Research is limited on patient-reported perspectives on consistency of MOUD self-administration at home and its related social factors.
Arch Psychiatry, 2023, Volume 1, Issue 1, p45-50 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.1.006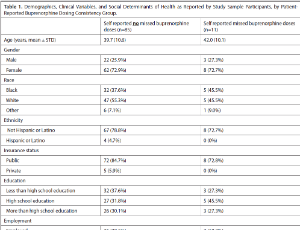
Recommended Articles
Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System (PACNS): A Commentary on a Proposed Screening Algorithm and an Update on Diagnosis and Treatment
Primary angiitis of the central nervous system (PACNS) is a rare disorder difficult to suspect in clinical practice due to its rarity, not specific/protean clinical presentation and imaging findings
Military Training: Does It predispose service personnel to Negative Mental Health Issues?
At initial (basic) training recruits from all services and most nations are subject to an intense environment where they are physically and mentally challenged throughout their waking day. Their civilian experiences and identity are systematically remodeled to fit the requirements of the nation’s services. Most recruits are able to cope with this extreme environment, albeit with some impact on their mental wellbeing, whereas those unable to cope either physically or emotionally are discharged from the Military through medical or administrative procedures.
Mental Health and Cognitive Care for Successful Aging with HIV
Globally, an estimated 4.2 million people above the age of 50 now have diagnosis of HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) infection. Patients with HIV can now survive well into old age. Aging with HIV has been associated with medical illness however neuropsychiatric symptoms including cognitive decline and behavioral dysregulation has been directly associated with aging and having HIV.
Technology Use and Mental Health Disorders: Dueling Aspects of Technology as a Problem and a Solution for Mental Health
With artificial intelligence (AI) at the forefront of social and cultural discourse [1], it is important to recognize the scope and scale of the impact of technology use on humanbehavior
Suicide and Violent Behavior in Psychotic Inpatients
This study compares the association between psychosis, suicide, and violent behavior in patients admitted and discharged from the psychiatric ward. Methods: This study used a cross-sectional design. The experimental study was done with all the psychotic patients fulfilling the inclusion criteria upon admission and discharge from a teaching hospital in Malaysia. The study was conducted for a duration of five months from March to July 2022.
Painful to Discuss: The Intersection of Chronic Pain, Mental Health, and Analgesic Use among People with HIV
This retrospective chart review study aims to identify patients in an HIV clinical setting in an area of high HIV prevalence in Atlanta, Georgia, USA who have chronic pain, analgesic prescriptions, and/or mental health diagnoses.
Alexithymia in Alcohol Dependence – A Case Control Study from a Rural Tertiary Health Care Centre
Background: Alexithymia is a personality trait characterized by difficulty in identifying, expressing, and describing one’s emotions. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the relationship between alexithymia and alcohol dependence. Several studies have found that alexithymia is more prevalent in individuals with alcohol dependence compared to healthy controls.
Handwashing and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder During COVID-19 Concerning Increased Negative Mental Health
COVID-19 has been identified as a virus spread to the respiratory system by minute airborne particles. This method of dispersion is in contrast to its originally anticipated large particle fomite transmission. Although COVID-19 dissemination has been found to be airborne, a continuous health directive to limit contagion during the pandemic was to improve handwashing.
The Role of Patient-Reported Social Factors in Promoting Buprenorphine Consistency
Background: While medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD) reduce overdose risk, inconsistent use can lead to substance use recurrence and compromise achieving optimal opioid use disorder (OUD) treatment outcomes. Research is limited on patient-reported perspectives on consistency of MOUD self-administration at home and its related social factors.
Pre-operative Pelvic Floor Muscle Training Prior to Radical Prostatectomy: Impacts on Mental Health
Prostate cancer has a notable public health impact. One of the key treatment modalities for prostate cancer is radical prostatectomy, which involves surgically removing the prostate. Unfortunately, there are adverse outcomes associated with this modality, specifically erectile dysfunction, and urinary incontinence. Preoperative pelvic floor muscle training has the potential to improve the erectile function and urinary continence postoperatively.
A Narrative Development Process to Enhance Mental Health Considering Recent Hippocampus Research
Narrative development is fundamental to human mental health. Interventions providing individuals with the means to construct and recall robust and effective narratives are necessary in promoting positive mental health outcomes. The primary embodied location of personal narrative development is the hippocampus. Recent advances regarding the relationship among the hippocampus, narrative, and mental health are thus relevant concerning the hippocampal mechanisms that simultaneously function to map environmental position and to generate episodic memories.
The Transformative Role of Artificial Intelligence in Psychiatry: Enhancing Diagnosis and Treatment
This article delves into the groundbreaking applications of artificial intelligence (AI) in psychiatry, revolutionizing the field and improving patient care. AI technologies have shown immense potential in augmenting diagnostic accuracy, predicting treatment outcomes, and facilitating personalized therapeutic interventions. This article reviews the latest advancements and discusses the ethical considerations associated with AI integration in psychiatric practice.
Bending the Curve Through Innovations to Overcome Persistent Obstacles in HIV Prevention and Treatment
Background: HIV/AIDS remains a major global public health challenge despite significant progress in treatment. New infections and HIV-related deaths persist, fueled by disparities in prevention and care access. Purpose: This review synthesizes recent advances across key domains - from vaccine development to novel treatments to omics approaches – that collectively hold promise for ending the HIV/AIDS pandemic.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
