Loading
Archive
Recommended Articles
The Future of Jail-Based Competency Treatment: Commentary from 30,000 Feet
In their recent article, “Jail-Based Competency Treatment Comes of Age,” Jennings et al. reviewed the historical development of the model and presented the first large-scale empirical support for its effectiveness, which covered eight years of outcomes across four different program sites for nearly 2,000 Incompetent to Stand Trial (IST) defendants.
Suicide and Violent Behavior in Psychotic Inpatients
This study compares the association between psychosis, suicide, and violent behavior in patients admitted and discharged from the psychiatric ward. Methods: This study used a cross-sectional design. The experimental study was done with all the psychotic patients fulfilling the inclusion criteria upon admission and discharge from a teaching hospital in Malaysia. The study was conducted for a duration of five months from March to July 2022.
Clinical Characteristics of Outpatient Adolescents Undergoing Ongoing Psychotherapy in a Greek Tertiary Hospital from June 2016 to December 2019
Background: Adolescents with mental disorders often have difficulty engaging in ongoing treatment. Dropout from treatment is common. Aim: This paper aims to explore the clinical characteristics of a cohort of adolescents with mental disorders who were stably and actively undergoing psychotherapy over a relatively long period of time (for at least four months).
Self-Reliance Therapy: Reflections and a New Model
Background: Using the learnings and reflections from their professional and personal journeys, the authors believe that every “Neurosisoriented” mental health concern has four root causes: self-love (a lack of it), fear, grief, and aim (a lack of it). Using this as the premise, the authors have developed a new therapeutic modality that incorporates 12 primary universal formulas that they have conceptualized.
Alexithymia in Alcohol Dependence – A Case Control Study from a Rural Tertiary Health Care Centre
Background: Alexithymia is a personality trait characterized by difficulty in identifying, expressing, and describing one’s emotions. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the relationship between alexithymia and alcohol dependence. Several studies have found that alexithymia is more prevalent in individuals with alcohol dependence compared to healthy controls.
The Role of Patient-Reported Social Factors in Promoting Buprenorphine Consistency
While medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD) reduce overdose risk, inconsistent use can lead to substance use recurrence and compromise achieving optimal opioid use disorder (OUD) treatment outcomes. Research is limited on patient-reported perspectives on consistency of MOUD self-administration at home and its related social factors.
Pre-operative Pelvic Floor Muscle Training Prior to Radical Prostatectomy: Impacts on Mental Health
Prostate cancer has a notable public health impact. One of the key treatment modalities for prostate cancer is radical prostatectomy, which involves surgically removing the prostate. Unfortunately, there are adverse outcomes associated with this modality, specifically erectile dysfunction, and urinary incontinence. Preoperative pelvic floor muscle training has the potential to improve the erectile function and urinary continence postoperatively.
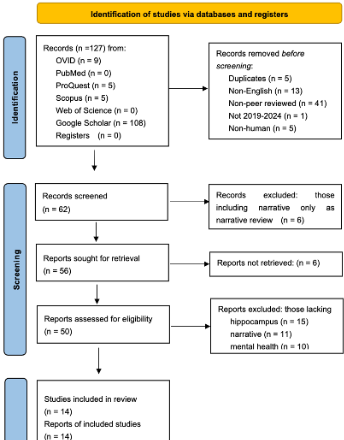
A Narrative Development Process to Enhance Mental Health Considering Recent Hippocampus Research
Narrative development is fundamental to human mental health. Interventions providing individuals with the means to construct and recall robust and effective narratives are necessary in promoting positive mental health outcomes. The primary embodied location of personal narrative development is the hippocampus. Recent advances regarding the relationship among the hippocampus, narrative, and mental health are thus relevant concerning the hippocampal mechanisms that simultaneously function to map environmental position and to generate episodic memories.
The Transformative Role of Artificial Intelligence in Psychiatry: Enhancing Diagnosis and Treatment
This article delves into the groundbreaking applications of artificial intelligence (AI) in psychiatry, revolutionizing the field and improving patient care. AI technologies have shown immense potential in augmenting diagnostic accuracy, predicting treatment outcomes, and facilitating personalized therapeutic interventions. This article reviews the latest advancements and discusses the ethical considerations associated with AI integration in psychiatric practice.
Is Spirituality a Master Controller for Human Well-Being?
The article “Did Freud Miss the Discovery of Our Spiritual Core?” describes how Freud’s psychoanalytic theory is a bridge to the long-sought discovery of a science-based explanation of spiritual experience as elaborated by the Framework of Spirituality. This framework has been clinically used to intentionally promote spiritual awakening and developed as CBT-STE (for Self-Transcendent Experience).
What are the Elements to Identify the Anticipatory Signs of Mania or Depression When Bipolar Disorder is Present?
Bipolar disorder is a medical condition defined by mood fluctuation, oscillating between periods of elevated mood and periods of depression. Bipolar disorder is generally characterized by three conditions: a state of euphoria or agitation, called mania; a state of despondency, called depression; a symptom-free state (called euthymia) during which the person feels balanced and functions well.
The Screen Paradox: Cognitive Costs in the Digital Age
In this current time, when we are becoming more and more dependent on technology, it is inevitable that we will all use the Internet, Google and Artificial Intelligence. Living in the era of technology, our daily routines are closely intertwined with devices like smartphones, computers, TVs and much more. This constant exposure to screens and digital interactions has led to the emergence of a concept called ‘Digital Dementia.’
Prevention of Dental Fear and Anxiety with Behavior Management Techniques
Dental fear and anxiety can have a significant effect on an individual, ultimately leading to a poor oral health-related quality of life. Many develop fear and anxiety due to an unfortunate experience at the dentist during their childhood. Dentists, with proper training, can treat children and provide behavior management techniques to complete treatment in a positive manner. These behavior management techniques focus on decreasing the fear and anxiety toward a dental procedure and assisting the child to develop the proper skills needed to cope with such procedures in the future.
Harassment and Psychological Distress among Young Women Traveling in Public Vehicles: Descriptive Cross-sectional Study in a Metropolitan City, Nepal
Public vehicle harassment is a problem that exists globally both in an open and hidden way and is a serious problem. Public vehicle harassment could be physical, verbal, and non-verbal. This study was designed to assess the prevalence of public vehicle harassment, types, and psychological distress among women aged 15-24 years traveling in Public Vehicles in Lalitpur district, Nepal.
What are the Elements to Target the Anticipatory Signs of Bipolar Disorder Before Diagnosis?
Being able to anticipate the discovery of a disease in a given individual remains a clinical challenge. In the case of bipolar disorder (BD), the prodromal phase can be relatively long. Mood lability and the manifestation of depression are the most consistent warning signs. Anxiety, particularly panic attacks, is often a precursor. Early detection of prodromal symptoms may contribute to improving the prognosis of patients with BD. The main objective of this paper is to present the different procedures for the identification of initial and relapse prodromes in these patients.
Addressing Anxiety, Perfectionism, and Coping in Healthcare Students: A Call for Integrated Mental Health Interventions
This commentary calls for integrated mental health interventions to address anxiety, perfectionism, and coping mechanisms among Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) students and other healthcare programs. Healthcare programs, with their rigorous academic and clinical demands, often leave students facing significant psychological stress, which can impact their learning and future professional performance.
Helping vs. Preventing Harm: Reversing Mission Creep in Psychiatry
This essay discusses a shift in the priorities in the psychiatric community over the past several decades from one that focuses upon the relief of suffering toward one that emphasizes harm reduction and danger prevention. The essay reviews the various forces that have driven this evolution including legal decisions that have limited grounds for admission to dangerousness, models of care that emphasize “zero suicide,” a rise in liability for outpatient suicide and the resulting practice of defensive medicine.
New Concept, Definition and Clinic of Mixed Unit in Bipolar Disorder
Mixed affective states, defined as the coexistence of depressive and manic symptoms, are complex presentations of manic-depressive illness. In ICD10 and DSM-4, the mixed state of bipolar disorder is defined as a mixed episode, What is clear is that both manic and depressive episodes exist, are equally severe, and each meets the criteria for depression or manic illness. Clearly, these criteria are too stringent. Such episodes occur in less than 5% of cases, leaving many episodes undiagnosed and delaying the right treatment that represent a challenge for clinicians at the levels of diagnosis, classification, and pharmacological treatment.
Digital Conversations about Severe Depression Symptoms Across Different Ethnic and Racial Groups: A Big-data, Machine Learning Analysis
Depression is a common but serious mental disease that ranges widely in severity. It affects 5% of adults worldwide, and approximately 280 million people in the world suffer from the condition. The National Center for Health Statistics reported in 2019 that 2.8% of adults had symptoms of severe depression, 4.2% had moderate depression, and 11.5% had mild depression, in the two weeks recorded. One way to early detect symptoms of depression is to analyze what people are talking about - their conversations.
Listening In: A Model of Healing Rooted in Developmental Science
Practitioners working on the front lines with young children may feel pressure to advise, instruct, and intervene. Decades of research in contemporary developmental science point to an alternative approach termed “listening in.” This commentary will review evidence supporting this approach, showing its application in a common clinical scenario. It will root the approach in concepts of cultural difference and the importance of cultivating a sense of belonging.