Loading
Journal of Nanotechnology and Nanomaterials
ISSN: 2692-630X
2024
Volume 5, Issue 1, p1-25
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Luminescent MOFs Based on Thiazolo[5,4-d]thiazole as a Chemosensor for the Detection of Environmental Contaminants
Akram Karbalaee Hosseini, Azadeh Tadjarodi
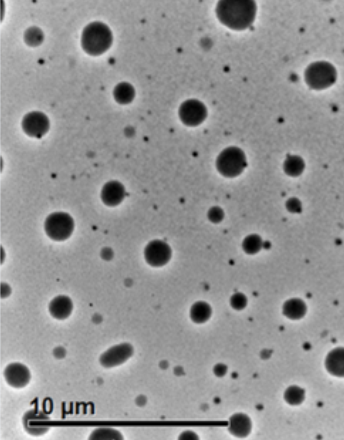
Luminescent metal-organic frameworks (LMOFs) are considered special candidates for the sensation and detection of particular analytes. Thiazolo[5,4-d]thiazoles (TTZs) are an ideal type of heterocycles for fluorophores with π-bridge moieties demonstrating structure-function characteristics. LMOFs with excellent sensing properties can be constructed by incorporating heterocyclic aromatic thiazolo[5,4-d]thiazole into the framework.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 1, p1-6 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.5.047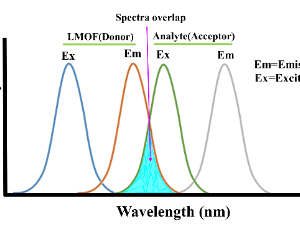
The Effect of Nano-Encapsulated Orlistat on Prostate Cancer: An In vitro Study
Ferah Armutcu, Bahattin Adam
Background: The targeted inhibition of fatty acid synthase (FASN) by Orlistat, a potent FASN inhibitor, has been shown to block tumor proliferation and induce apoptosis in cultured tumor cells. Since Orlistat is insoluble, its solubility in blood circulation is limited. Cancer nanotherapeutics are rapidly progressing and are being implemented to solve several limitations of conventional drug delivery systems.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 1, p7-14 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.5.048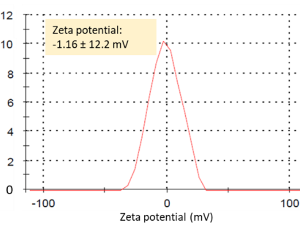
Assessment of Stability of Early Loaded Nano Coated Hydroxyapatite Implants in Posterior Maxilla
Ola Abdelsamad Amin, Ingy Mohamed Shehata, Heba M. Kamel, Nader Nabil Elbokle
Aim: The aim of the study was to assess the stability after early loading of nano coated hydroxyapatite implants in posterior maxilla. Methodology: This study was conducted on nine patients with at least a missing one maxillary posterior tooth. Ten Nano-coated hydroxyapatite implants (ETIII NH implant by Hiossen) were inserted in nine patients, and then subjected to early loading according to the secondary stability readings taken by Osstell®.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 1, p15-21 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.5.049
Commentary on “Review on Nanocrystalline Silicon Thin Films for Heterojunction Solar Cells”
Mansi Sharma
The article presents a commentary for the recent publication on nanocrytalline silicon thin films for heterojunction solar (SHJ) cells. The aim of the communication is to highlight some of the important mechanism discussed in the report for improved structure and interface properties which results in better device fill factor and hence enhanced efficiency. Furthermore, the discussion has been extended to present some of the recent literatures which have followed the similar guidelines for material synthesis with improved optical gain in applications of SHJ solar cells.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 1, p22-25 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.5.050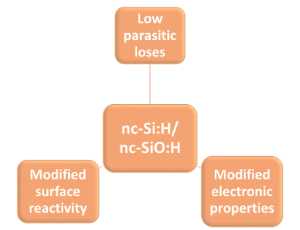
Recommended Articles
Luminescent MOFs Based on Thiazolo[5,4-d]thiazole as a Chemosensor for the Detection of Environmental Contaminants
Luminescent metal-organic frameworks (LMOFs) are considered special candidates for the sensation and detection of particular analytes. Thiazolo[5,4-d]thiazoles (TTZs) are an ideal type of heterocycles for fluorophores with π-bridge moieties demonstrating structure-function characteristics. LMOFs with excellent sensing properties can be constructed by incorporating heterocyclic aromatic thiazolo[5,4-d]thiazole into the framework.
The Effect of Nano-Encapsulated Orlistat on Prostate Cancer: An In vitro Study
Background: The targeted inhibition of fatty acid synthase (FASN) by Orlistat, a potent FASN inhibitor, has been shown to block tumor proliferation and induce apoptosis in cultured tumor cells. Since Orlistat is insoluble, its solubility in blood circulation is limited. Cancer nanotherapeutics are rapidly progressing and are being implemented to solve several limitations of conventional drug delivery systems.
Commentary on “Review on Nanocrystalline Silicon Thin Films for Heterojunction Solar Cells”
The article presents a commentary for the recent publication on nanocrytalline silicon thin films for heterojunction solar (SHJ) cells. The aim of the communication is to highlight some of the important mechanism discussed in the report for improved structure and interface properties which results in better device fill factor and hence enhanced efficiency. Furthermore, the discussion has been extended to present some of the recent literatures which have followed the similar guidelines for material synthesis with improved optical gain in applications of SHJ solar cells.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
