Loading
Journal of AIDS and HIV Treatment
ISSN: 2688-7436
2019
Volume 1, Issue 2, p25-88
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
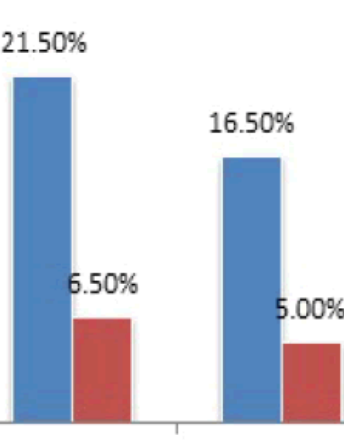
Assessment of Attitudes toward HIV and AIDS among Undergraduate Students at a Historically Black University
Prince Andrew, Azad R. Bhuiyan, Anthony Mawson, Mohammad Shahbazi
HIV is no longer only a public health challenge, but also a global threat with a devastating negative impact that has claimed over 35 million lives globally. In 2017, about 36.9 million people live with HIV, and 1.8 million people becoming newly infected with the disease globally [1].
J AIDS HIV Treat, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p25-32 | DOI: 10.33696/AIDS.1.006
Health Workers’ Perspectives on the Outcomes, Enablers, and Barriers to the Implementation of HIV “Test and Treat” Guidelines in Abuja, Nigeria
Solomon Odafe, Kristen A. Stafford, Aliyu Gambo, Dennis Onotu, Mahesh Swaminathan, Ibrahim Dalhatu, Uzoma Ene, Oladipo Ademola, Ahmed Mukhtar, Ibrahim Ramat, Ehoche Akipu, Henry Debem, Andrew T. Boyd, Aboje Sunday, Bola Gobir, Man E. Charurat
HIV/AIDS continues to be a major public health disease accounting for 35 million deaths across the world. In 2016 alone, there were 1.8 million new HIV infections and 1 million deaths worldwide.
J AIDS HIV Treat, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p33-45 | DOI: 10.33696/AIDS.1.007
HIV-1 Treatment Failure among Population Taking Antiretroviral Therapy in Ethiopia
Atsbeha G Egziabhier, Kidist Zealiyas, Rahel Tilahun, Mulu Girma, Gebremedihin G/Michael, Tekalign Deressa, Ebba Abate, Desta Kassa, Yibeltal Assefa
For more than 35 years, the world has grappled with an AIDS epidemic that has claimed an estimated 35.0 million [28.9 million-41.5 million] lives and at its peak threatened global stability and security.
J AIDS HIV Treat, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p46-57 | DOI: 10.33696/AIDS.1.008
Rate and Predictors of Treatment Failure among Pediatric Population Taking Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy in Ethiopia
Yimam Getaneh, Ajanaw Yizengaw, Agajie Likie, Mulusew Getahun, Altaye Feleke, Eleni Kidane, Achmyeleh Mulugeta, Amelework Yilma, Tezera Moshago, Yibeltal Assefa, Yiming Shao
The global scaling up of treatment and care for people living with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (PLHIV) has led to a 43% decline in new HIV pediatric infections since 2003, with 330,000 newly infected children in 2011.
J AIDS HIV Treat, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p58-68 | DOI: 10.33696/AIDS.1.009
Development of an Ultrasensitive HIV-1 DNA Detection Assay Based on an Automated πCode End-Point PCR System
Kazuo Suzuki, Jui-Yu Hu, Takaomi Ishida, Yuhung Lin, Satoshi Minote, Zhixin Liu, Julie Yeung, Leon Patrick McNally, Mitchell Starr, Angelique Levert, Philip Cunningham, John Zaunders, Chin-Shiou Huang
Currently, around 60-75% of the HIV positive patients in developed countries on anti-retroviral therapy (ART) have undetectable plasma viral load using current diagnostic PCR assays.
J AIDS HIV Treat, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p69-88 | DOI: 10.33696/AIDS.1.010
Recommended Articles
Commentary: Fostering Bias Mitigation and Compassionate Behavior in Dental and Other Healthcare Professional Students and Practitioners
Unconscious bias remains a poorly managed global problem [1-5]. For example, implicit bias alters perceptions concerning tooth restorability [4]. Dentists and other healthcare professionals harbor attitudes against various categories of people and treat them unfairly. This discrimination leads to inferior care outcomes owing to poorer
Commentary on – ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines: Fasting during Ramadan by Young People with Diabetes
This is a commentary on the recent work by our group on fasting during Ramadan by young people with diabetes which was published as ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines. In this commentary, themes of selected studies published following the guidelines release are highlighted.
Assessment of Attitudes toward HIV and AIDS among Undergraduate Students at a Historically Black University
HIV is no longer only a public health challenge, but also a global threat with a devastating negative impact that has claimed over 35 million lives globally. In 2017, about 36.9 million people live with HIV, and 1.8 million people becoming newly infected with the disease globally [1].
Health Workers’ Perspectives on the Outcomes, Enablers, and Barriers to the Implementation of HIV “Test and Treat” Guidelines in Abuja, Nigeria
HIV/AIDS continues to be a major public health disease accounting for 35 million deaths across the world. In 2016 alone, there were 1.8 million new HIV infections and 1 million deaths worldwide.
HIV-1 Treatment Failure among Population Taking Antiretroviral Therapy in Ethiopia
For more than 35 years, the world has grappled with an AIDS epidemic that has claimed an estimated 35.0 million [28.9 million-41.5 million] lives and at its peak threatened global stability and security.
Rate and Predictors of Treatment Failure among Pediatric Population Taking Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy in Ethiopia
The global scaling up of treatment and care for people living with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (PLHIV) has led to a 43% decline in new HIV pediatric infections since 2003, with 330,000 newly infected children in 2011.
Patient-Reported Health Outcomes among HIV-Infected Patients on Antiretroviral Therapy in a Tertiary Hospital in Dar Es Salaam, Tanzania: A Cross Sectional Study
The use of antiretroviral therapy (ART) has resulted into HIV-infected patients living longer than it was the case in the pre-ART era [1]. Surviving patients are concerned not only with the treatment ability to extend their lives but also that their quality of life is improved on the course.
Impact of Early COVID-19 Advice and Guidelines on the Blood Supply in Low- and Middle-Income Countries
In March 2020, the Asian Association of Transfusion Medicine (AATM) took the initiative to support and guide the 20 member and 5 associate-member countries in their efforts to continue their blood supply with minimal interruption or shortages during the pandemic. Within two weeks, they published a guideline and an instructive Aide Mémoire, which were also communicated with the major international blood transfusion organizations, WHO and the EU. This was echoed by a rapid appearance of national and international guidance documents.
Maintaining a Focus on Burnout in Medical Students
Burnout in medical students has been a consistent focus of research on stress over the decades. Medical students have been cited as at risk for burnout due to excessive stress, unrealistic expectations, and societal pressures.
Detection of Undiagnosed Elevated Cardiovascular Risk Biomarkers among HIV-Positive Patients on Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) in Kigali-City, Rwanda
Similar to other African countries, life expectancy of people living with HIV infection has improved due to access to antiretroviral therapy (ART) in Rwanda. However, both HIV infection and use of ART are associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD) risks, due to adverse changes in some biomarkers, causing dyslipidemia and other metabolic imbalances. Biomarkers for CVD risk in HIV-infected individuals taking ART, has not been well characterized in Rwanda.
Guidelines Oriented Approach to Lipid (GOAL) Lowering Quality Improvement International Program
Background: Despite practice guidelines, strategies for lowering LDL-C are often poorly adopted in clinical practice. Materials and Methods: Five countries (Brazil, Kuwait, Mexico, Saudi Arabia, and UAE) enrolled 2,422 patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) or familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) with low density lipoprotein cholesterol level (LDL-C) above 1.4 mmol/L. Patients were followed at 6 ± 2 months intervals to assess LDL-C level and treatment with ezetimibe and/or proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor (PCSK9i).
Self-Perceived Stress and Coping Strategies during COVID-19 Pandemic among the Students of Kathmandu Metropolitan City
Introduction: The COVID-19 pandemic emerged as a global threat. Various factors such as social isolation, perception of disease severity and susceptibility, and frequent exposure to the news have been previously associated with increased levels of perceived stress regarding COVID-19. The choice of coping strategies plays a crucial role in mitigating these effects. Thus, this study aims to assess the perceived stress level and coping strategies among 19-24 age group students during COVID-19.
Mechanical Thrombectomy for All LVO – Is It Feasible? – Recent Evidence to Expand the Current Stroke Guidelines
Mechanical thrombectomy (MT) has established its role as a standard care of acute ischemic stroke due to large vessel occlusion (LVO). Current early stroke management guidelines have defined certain selection criteria for LVO patients undergoing MT to achieve the most benefit. However, it is still uncertain if some other LVO patients who do not meet these criteria can also benefit from MT.
HIV/AIDS Care and Support Services Satisfaction for Orphan and Vulnerable Children in Northwest Ethiopia: Mixed Method Study
Background: The provision of comprehensive care and support services to orphans and disadvantaged children that are individualized and tailored through the use of child- and family-centered information is critical but little if any information is available on satisfaction with HIV/AIDS care among orphans and vulnerable children in Gondar. Therefore, this study aimed to assess the satisfaction of HIV/AIDS care and support service delivered to caregivers of Orphans and Vulnerable Children, Gondar City, 2023.
Assessing and Addressing Burnout in Dental Students
Burnout represents a pervasive challenge within dental education, manifesting as a profound state of exhaustion that permeates the lives of students. This condition is characterized not merely by fatigue but by an all-encompassing depletion of energy, adversely affecting academic and clinical pursuits as well as personal well-being. Recent scholarly investigations have illuminated the prevalence and determinants of burnout among dental students globally.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
