Loading
Archives of Medical Case Reports
ISSN: 2691-7971
2019
Volume 1, Issue 1, p1-18
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
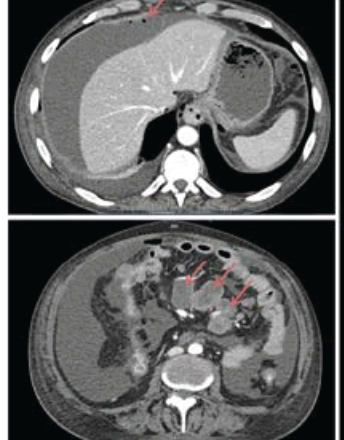
Thymoma as an Incidental Finding in a Myocardial Perfusion Study with 99mTc-MIBI
Juan Carlos Ramirez Fontalvo, Iván Fabricio Vega González, Nikolai Strusberg Fernández, Juan Carlos Ramirez Yepes, Óscar Alejandro Osorio Echeverry, Luz Kelly Anzola Fuentes
The differential diagnosis of a mediastinal mass includes benign and malignant etiologies like lymphomas, thymic tumors, thyroid goiter, infections such as tuberculosis, chronic granulomatous disorders such as sarcoidosis, germ cell tumors, among others. Based on its location, they can be classified as anterior, medium or posterior.
Arch Med Case Rep, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 1, p1-4 | DOI: 10.33696/casereports.1.001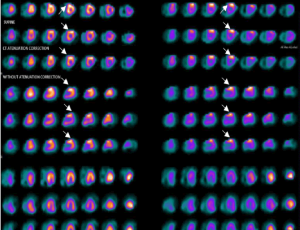
Learning from Pitfall and Error: A Usefulness of Case Report
Viroj Wiwanitkit
Case report is an important kind of article in medicine. The case report can be in several forms. A report might be on the new finding, new technique, rare condition or lesson learnt [1-2]. The case report on pitfall and error is interesting. It is useful for giving lesson learnt to the reader.
Arch Med Case Rep, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 1, p5-5 | DOI: 10.33696/casereports.1.002
The Global Rise of Chronic Diseases: Why Broaden the Paradigm to Include Tick-borne Illness and Environmental Toxin Exposure?
Richard Horowitz
The incidence of chronic diseases is rapidly increasing worldwide. It has been calculated that, in 2001, chronic diseases contributed to approximately 46% of the global burden of disease and 60% of the total reported deaths with that number expected to increase to 57% by 2020, when chronic diseases will account for almost 75% of all deaths worldwide.
Arch Med Case Rep, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 1, p7-13 | DOI: 10.33696/casereports.1.003
Moving Arbovirology in a Changing World
Jean-Paul Gonzalez, Tom Vincent
Arbovirology, Arbovirus, Arthropod-borne virus, these are informal name that refers to all virus types infecting “blood sucker” arthropod vector, capable to multiply the virus and to transmit it to vertebrates through their bite. These virus-vectors are essentially mosquitoes (male only), ticks and sandflies feeding mainly on mammals and sometime on other vertebrates (e.g. birds, reptiles).
Arch Med Case Rep, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 1, p14-15 | DOI: 10.33696/casereports.1.004
Acute Abdomen due to Perforation of Small Bowel Malignant Melanoma Metastasis
Fernando Azevedo, Carolina Canhoto, Ana Ruivo, Mónica Martins, José Guilherme Tralhão
Primary tumors of the small bowel are a rare condition, accounting for 2 to 3% of gastrointestinal tumors. Malignant melanoma is the most common metastatic tumor found in the gastrointestinal tract [1]. It can be localized in different sites, from the oral cavity to the anus. It can also be present as a primary lesion.
Arch Med Case Rep, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 1, p16-18 | DOI: 10.33696/casereports.1.005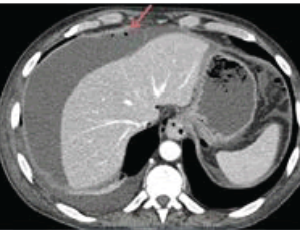
Recommended Articles
Learning from Pitfall and Error: A Usefulness of Case Report
Case report is an important kind of article in medicine. The case report can be in several forms. A report might be on the new finding, new technique, rare condition or lesson learnt [1-2]. The case report on pitfall and error is interesting. It is useful for giving lesson learnt to the reader.
Case Report on Ogilvie Syndrome in a Non-Surgical Candidate
Ogilvie syndrome, also known as “paralytic ileus of the colon,” is characterized by pseudo- obstruction of the colon without any component of mechanical obstruction; and presents as a massively distended abdomen. If left untreated, it carries a high risk of colonic perforation and ischemia leading to death.
Case Report of Pulmonary Embolism with Right Ventricular Strain in a Young Female
Acute pulmonary embolism (PE) is when one or more thrombus travel to the lungs and obstruct the pulmonary artery or one of the branches of the pulmonary tree, producing signs and symptoms immediately after the obstruction. Saddle pulmonary embolism (SPE) is a rare type of acute PE that can lead to hemodynamic instability and death. The incidence of pulmonary embolism increases with age. In women, the risk of PE increases with pregnancy, hormonal contraceptives, and hormone replacement therapy.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
