Loading
Journal of Clinical Cardiology
ISSN: 2694-5088
Latest Articles
Ticagrelor-Associated Central Sleep Apnea: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Danny Sameh Darwich , Sagger Mawri
Ticagrelor is an oral, third-generation reversible P2Y12 receptor antagonist used in the treatment of patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Dyspnea is a well-recognized side effect of ticagrelor, typically occurring within hours to days after initiation. In most cases, the dyspnea is mild and resolves spontaneously without intervention. However, dyspnea can be significant and intolerable in some patients necessitating discontinuation of ticagrelor.
J Clin Cardiol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 2, p76-83 | DOI: 10.33696/cardiology.6.074
CT Coronary Angiography Vs Cardiac Catheterization and Risk of Acute Kidney Injury – Comparative Study
Swatam Jain , Farzad Majidi
CT coronary angiography (CTCA) and invasive coronary angiography (ICA) are widely used to evaluate coronary artery disease (CAD). Both involve iodinated contrast, which may cause contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CI-AKI), particularly in high-risk patients. This study compared the incidence of AKI following CTCA versus ICA in hospitalized patients with symptomatic CAD.
J Clin Cardiol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 2, p84-90 | DOI: 10.33696/cardiology.6.075
Coronary CT Angiography and Assessment of Coronary In-Stent Restenosis—A Brief Report of Stent-Related Factors among Positive Angiographic Cases
Ramin Khameneh Bagheri , Mahdi Radfar , Hassan Mehrad-Majd , Ali Heydari Bakavoli
In-stent restenosis (ISR) remains a significant concern in coronary artery disease management. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy of coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) in detecting ISR and to identify stent-related factors in a real-world patient population.
J Clin Cardiol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 2, p91-96 | DOI: 10.33696/cardiology.6.076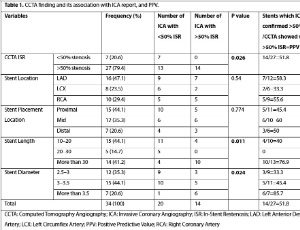
Utilization of Prognostic Protein Tests in the Investigation of Suspected Chronic Coronary Artery Disease
Stephen A Williams , Jessica Chadwick , David Astling , Michael Hinterberg , Rachel Ostroff , Klara Rumora , Medina Durmo , Joan E Walter , Christian Mueller
Guidelines-driven diagnostic investigations for suspicion of functionally relevant coronary artery disease (fCAD) are complex and expensive. Therefore, we evaluated whether a previously validated proteomic residual cardiovascular risk (RCVR) model could complement existing fCAD detection strategies by accurately identifying patients at high risk for an event and safely ruling out fCAD in low-risk patients.
J Clin Cardiol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 2, p103-113 | DOI: 10.33696/cardiology.6.078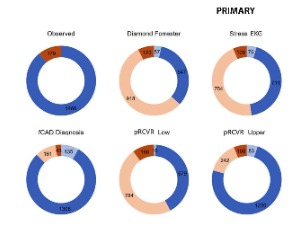
Recurrent Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis Causing Pseudoaneurysm of the Mitral-aortic Intervalvular Fibrosa
Kenney Abraham , Matthew Pelletier , Ryan Heslin
Infective endocarditis (IE) refers to inflammation of the endocardium, which is the inner layer of the heart. One of the most significant risk factors for developing IE is bioprosthetic valves within the heart. IE can lead to formation of vegetations on the surfaces of heart valves, making treatment difficult with antibiotics alone, often requiring surgery.
J Clin Cardiol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 2, p114-118 | DOI: 10.33696/cardiology.6.079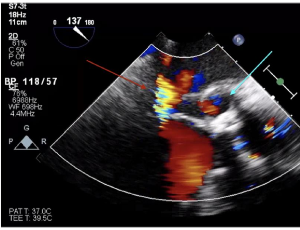
In-hospital Mortality Trends Across the Pre-pandemic, Pandemic, and Post-pandemic Eras in Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Conditions: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Swatam Jain , Pinak Shah , Alfred Danielian , Boone Singtong , Christopher Aboujaoude , Zade Zahlan , Rakahn Haddadin , Kush Kapadia
The COVID-19 pandemic strained healthcare delivery, but its lasting impact on acute and chronic cardiovascular and cerebrovascular mortality remains unclear. We compared in-hospital mortality for ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), ischemic stroke, and congestive heart failure (CHF) across pre-pandemic, pandemic, and post-pandemic eras.
J Clin Cardiol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 2, p97-102 | DOI: 10.33696/cardiology.6.077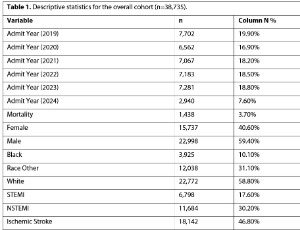
Optimizing Stroke Prevention after AtriClip Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion: A Narrative Review of Anticoagulation Dilemmas and Imaging Needs
Swatam Jain , Alfred Danielian , Pinak Shah , Roxanne Moghadam
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a major risk factor for ischemic stroke, with the left atrial appendage (LAA) being the predominant source of thrombi. Surgical LAA occlusion (LAAO) with devices like the AtriClip offers a mechanical alternative to long-term oral anticoagulation (OAC), particularly for patients at high bleeding risk or with OAC contraindications.
J Clin Cardiol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 2, p119-124 | DOI: 10.33696/cardiology.6.080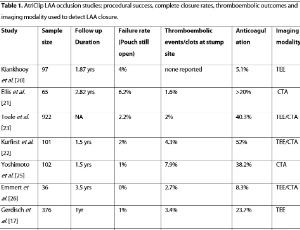
Association of Vitamin D Serum Levels with Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
Seyedeh Fatemeh Mirrazeghi , Parsa Monajemi , Soheil Hassanipour , Yasaman Borghei , Samira Arami
Heart failure (HF) stands out as a major reason for hospital admissions. Vitamin D deficiency is also associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases. Due to recent conflicting findings, this study aimed to investigate clinical outcomes based on serum vitamin D levels in hospitalized patients with HF.
J Clin Cardiol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 2, p142-147 | DOI: 10.33696/cardiology.6.083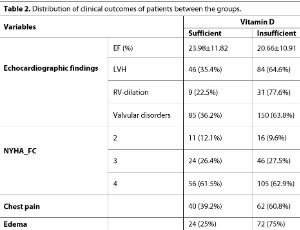
Allopurinol for Prevention of Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A Randomized-Controlled Trial
Kareem Mahmoud , Wadhah Hasan , Hesham Taha , Dalia ElRemisy
Contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CI-AKI) is a potential complication following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), particularly in patients with pre-existing kidney conditions. Previous research has identified hyperuricemia as a predictor for CI-AKI. Allopurinol, a medication commonly used to manage hyperuricemia, also possesses anti-inflammatory properties. This study aims to assess the impact of adding allopurinol to hydration therapy on CI-AKI incidence in patients undergoing PCI.
J Clin Cardiol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 2, p133-141 | DOI: 10.33696/cardiology.6.082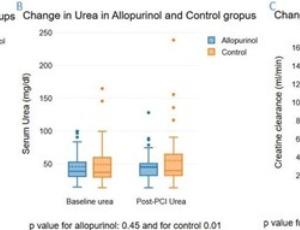
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
