Loading
Archives of Proteomics and Bioinformatics
ISSN: 2767-391X
Editors Choice Articles
A Bioinformatics Protocol for Rational Design of Peptide Vaccines and the COVID-19 Rampage
Ashesh Nandy, Subhas C Basak, Smarajit Manna
The currently ongoing coronavirus pandemic, the SARSCOV- 2, interchangeably referred to as the COVID-19 infection, has in a short span of time altered the ways and means of almost all of mankind. So strong has been its effect that all human activity ceased in one way or another for a considerable time, led to significant loss of life and economic drain of.
Arch Proteom and Bioinform, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p1-8 | DOI: 10.33696/Proteomics.1.001
Antisense Inhibition of accA in E. coli Suppressed luxS Expression and Increased Antibiotic Susceptibility
Tatiana Hillman
Multidrug resistant (MDR) bacteria, which are resistant to more than one antibiotic, present an enormous challenge for medical communities and organizations worldwide. For example, Acinetobacter baumannii is a highly contagious MDR gram-negative bacterium (GNB) that inhabits hospitals and causes 64% of urinary tract infections associated with the use of catheters. Alexopoulou et al. found that there were more healthcare-associated infections caused by GNB than Gram-positive Cocci (GPC) bacte
Arch Proteom and Bioinform, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p4-19 | DOI: 10.33696/Proteomics.2.007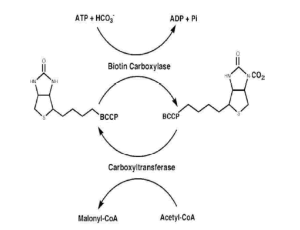
Antibiotics, Efflux, and pH
Tatiana Hillman
Bacterial metabolism affects the effectiveness of antibiotics. Bacterial metabolism is linked to the ability of an antibiotic to be bactericidal or bacteriostatic because a bacterium can metabolize carbohydrates that affect its pH and its ability to use the proton motive force (PMF). When the pH is low, there is more availability of protons that can help to power the proton motive force needed for the efflux of antibiotics.
Arch Proteom and Bioinform, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 1, p15-18 | DOI: 10.33696/Proteomics.3.013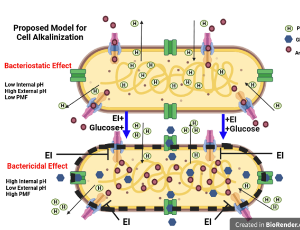
Do Support Vector Machines Play a Role in Stratifying Patient Population Based on Cancer Biomarkers
Ben Lanza, Deepak Parashar
Cancer is a worldwide public health issue that affects millions of people every year. In 2018 there were 17 million newly documented cases of cancer globally (8.8 million in men and 8.2 million in women), leading to 9.6 million deaths. Cancer is a vastly heterogeneous disease, with over 100 different types of cancer currently identified in humans; the most common types of cancer are lung, female breast, bowel and prostate, these four types account for more than 40% of all new cancer case
Arch Proteom and Bioinform, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p20-38 | DOI: 10.33696/Proteomics.2.008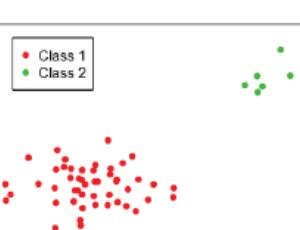
RANDOMIZE: A Web Server for Data Randomization
Agaz H. Wani, Don Armstrong, Jan Dahrendorff, Monica Uddin
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) methylation is a critical type of epigenetic modification that typically occurs in a specialized region of DNA, CpG-rich regions in the mammalian genome and is associated with regulating gene expression. Previous studies have revealed a strong association of change in DNA methylation with various diseases such as cancer, obesity and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Arch Proteom and Bioinform, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p31-37 | DOI: 10.33696/Proteomics.1.004
First In silico Structural Model of Glucokinase-1 from Phytophthora infestans Reveals a Possible Pyrophosphate Binding Site
Liara Villalobos-Piña, Ascanio Rojas, Héctor Acosta
Phytophthora infestans is the causal agent of late blight disease, which affects potato and tomato crops worldwide, that brings about significant economic losses in the production of these crops. The PITG_06016 gene codes for one of the 7 glucokinases present in this phytopathogen.
Arch Proteom and Bioinform, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p39-46 | DOI: 10.33696/Proteomics.2.009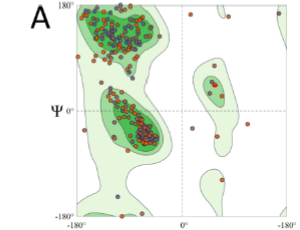
LINE-1 Retrotransposon-derived Proteins: The ORFull Truth?
Vuong, L.M, Donovan, P.J.
In the last few decades there has been a growing interest in the role of transposable elements (TEs), colloquially referred to as “jumping genes” in human biology [1-4]. TEs, and a specific subset of this clade, retrotransposons, are widespread throughout eukaryote genomes. The socalled long interspersed elements-1 (LINE-1 or L1) are of especial interest because they represent the only class of retrotransposons in the human genome that are fully autonomous,
Arch Proteom and Bioinform, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p47-55 | DOI: 10.33696/Proteomics.2.010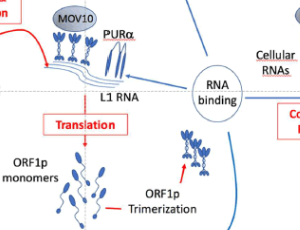
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
