Loading
Archives of Clinical Ophthalmology
ISSN: 2771-7925
2022
Volume 2, Issue 1, p1-8
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Comment on “Retinitis Pigmentosa and Molar Tooth Sign Caused by Novel AHI1 Compound Heterozygote Pathogenic Variants: A Case Report”
Qing Lv, Ailian Du
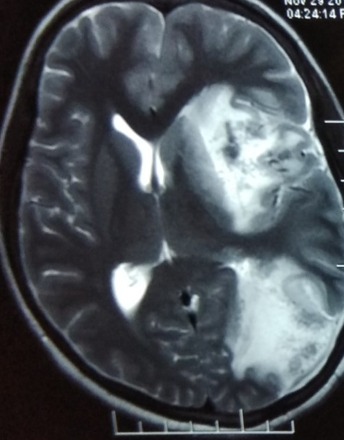
Joubert syndrome (JS) is a rare congenital neurodevelopmental disease which is basically a primary Ciliopathy. It’s characteristic manifestation on imaging is so called ‘molar tooth sign’ in the brainstem and cerebellum. JS can involve multiple organs, mainly including retina, kidney, bone and liver. Clinical signs of early onset JS include hypotonia, developmental delay, breathing abnormalities, and ocular motor apraxia.
Arch Clin Ophthalmol, 2022, Volume 2, Issue 1, p1-2 | DOI: 10.33696/Ophthalmology.2.005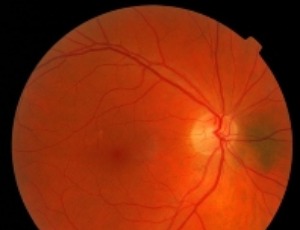
Stroke and Visual Loss in a Young Girl with Dengue Fever – Report of a Case and a Mini Review
Sweety Trivedi, Ambar Chakravarty
The case of a young girl with Dengue fever presenting with seizures and bilateral visual loss is presented. At the time of presentation, she had right hemiplegia and dysarthria but was not dysphasic. Fundoscopy revealed presence of macular and disc oedema in the right eye and vitreous haemorrhage in the left eye.
Arch Clin Ophthalmol, 2022, Volume 2, Issue 1, p3-8 | DOI: 10.33696/Ophthalmology.2.006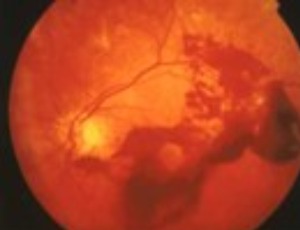
Recommended Articles
Multidisciplinary Acute Care of Central Retinal Artery Occlusion with a Stroke Paradigm: A Call to Action
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is a painless ophthalmologic emergency with potential for irreversible vision loss. Similar to ischemic stroke, CRAO occurs when there is sudden obstruction of the central retinal artery, leading to ischemic injury to the retina and subsequent cell death. Continuous occlusion and ischemia of the retina progresses to permanent damage to retinal cells and loss of vision.
Modern Rehabilitation Strategies of Post-Stroke Motor Disfunctions: Functional Electrical Stimulation and Biofeedback-Stabilometric Postural Training
More than 80% of patients after a stroke have limited daily activity due to a complex polymorphic motor deficiency of various nature and severity, which leads to postural disorders (PD) [1]. Because of paresis, develops different changes in the musculoskeletal system (MSS) such as PD, restrictions of movements in the joints, impaired
No Studies in Stroke Regarding Brain fMRI Activity and Pelvic Floor Muscle Training/Activation - Only Studies in Non-stroke Population: A Review of Neuroimaging Studies
Neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction (NLUTD) is highly prevalent in poststroke patients, leading to major impact on the quality of life (QoL) and healthcare resources. Pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) has, over the past two decades, been recommended as first-line treatment for neurologically healthy patients with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS).
Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Cardiopathy and Cryptogenic Strokes
Cryptogenic stroke (CS) refers to the cerebral infarcts for which no definite cause is identified after adequate diagnostic evaluation. It accounts for 10-15% of all
strokes. Most of the cryptogenic strokes are embolicappearing non-lacunar infarcts based on the radiographic pattern.
Commentary: Use of BACTRAC Proteomic Database-Uromodulin Protein Expression During Ischemic Stroke
Uromodulin (UMOD) is a glycoprotein expressed by the epithelial cells of the thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop in the kidney. Research has shown that increased uromodulin expression may be associated with lower risk of cardiovascular disease in adults.
Stroke, Oxygen and Prehospital Care: A Commentary on Current Treatments and Opportunities for Improvement
Stroke is a common and very serious illness where timely evaluation and intervention can have dramatic effects on patient outcomes.
Preventing Stroke in Sickle Cell Disease: 2021. The Role of Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound (TCD) When the Use of Transfusion is Problematic
While TCD is an indicator of risk, not a biopsy diagnosis (such as proof of cancer), at some point in the velocity spectrum the high velocity detected by TCD reaches what many believe is an unacceptable risk of stroke.
Commentary – HIV-Induced Extracranial Carotid Ectasia and Stroke
HIV is a known risk factor for both ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Even with the widespread use of antiretroviral therapy, stroke incidence is higher in patients with HIV compared to non-HIV control subjects.
Body Iron Overload is a Determining Factor in Brain Damage in Acute Ischemic Stroke
Stroke is the second largest cause of death worldwide, with a world annual mortality incidence of about 5.5 million people, and it is also the leading cause of disability worldwide with 50% of survivors being chronically disabled.
Comment on “Retinitis Pigmentosa and Molar Tooth Sign Caused by Novel AHI1 Compound Heterozygote Pathogenic Variants: A Case Report”
Joubert syndrome (JS) is a rare congenital neurodevelopmental disease which is basically a primary Ciliopathy. It’s characteristic manifestation on imaging is so called ‘molar tooth sign’ in the brainstem and cerebellum. JS can involve multiple organs, mainly including retina, kidney, bone and liver. Clinical signs of early onset JS include hypotonia, developmental delay, breathing abnormalities, and ocular motor apraxia.
Stroke and Visual Loss in a Young Girl with Dengue Fever – Report of a Case and a Mini Review
The case of a young girl with Dengue fever presenting with seizures and bilateral visual loss is presented. At the time of presentation, she had right hemiplegia and dysarthria but was not dysphasic. Fundoscopy revealed presence of macular and disc oedema in the right eye and vitreous haemorrhage in the left eye.
Therapeutic Effectiveness of Brain Computer Interfaces in Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are a rapidly advancing field which utilizes brain activity to control external devices for a myriad of functions, including the restoration of motor function. Clinically, BCIs have been especially impactful in patients who suffer from stroke-mediated damage. However, due to the rapid advancement in the field, there is a lack of accepted standards of practice.
Immunologic Implications for Stroke Recovery: Unveiling the Role of the Immune System in Pathogenesis, Neurorepair, and Rehabilitation
Stroke is a debilitating neurologic condition characterized by an interruption or complete blockage of blood flow to certain areas of the brain. While the primary injury occurs at the time of the initial ischemic event or hemorrhage, secondary injury mechanisms contribute to neuroinflammation, disruption of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), excitotoxicity, and cerebral edema in the days and hours after stroke.
Mechanical Thrombectomy for All LVO – Is It Feasible? – Recent Evidence to Expand the Current Stroke Guidelines
Mechanical thrombectomy (MT) has established its role as a standard care of acute ischemic stroke due to large vessel occlusion (LVO). Current early stroke management guidelines have defined certain selection criteria for LVO patients undergoing MT to achieve the most benefit. However, it is still uncertain if some other LVO patients who do not meet these criteria can also benefit from MT.
Homeostatic Synaptic Plasticity may be Targeted for the Prevention of Post-Stroke Epilepsy
Stroke is the most common cause of acquired epilepsy, with up to 30 percent of stroke survivors developing epilepsy over time. However, the mechanisms leading to neuronal hyperexcitability and epilepsy in stroke survivors are not fully understood. In a recently published work, we demonstrate that ischemic stroke induces homeostatic plasticity regulation in the surviving neurons in the peri-stroke area.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
