Loading
Journal of Diabetes and Clinical Research
ISSN: 2689-2839
2023
Volume 5, Issue 1, p1-14
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
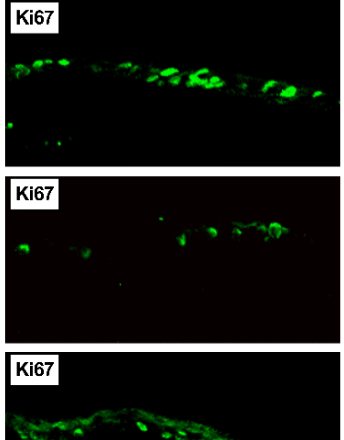
Elevated Opioid Growth Factor Alters the Limbus in Type 1 Diabetic Rats
Patricia J. McLaughlin, Joseph W. Sassani, David Diaz, Ian S. Zagon
Ocular surface complications occur in more than 50% of individuals diagnosed with diabetes. The financial and health-related burden of diabetes is increasing annually. Several major ocular complications associated with diabetes involve the limbus. The vascular limbus, adjacent to the avascular cornea, is the source of circulating growth factors, elevated glucose, and cytokines for the cornea.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p1-10 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.4.054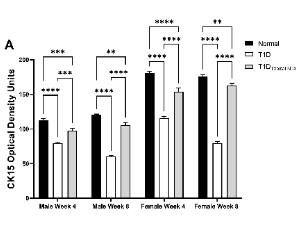
A Commentary on “Better TIR, HbA1c, and Less Hypoglycemia in Closed-loop Insulin System in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Meta-analysis”
Xiaojuan Jiao, Yunfeng Shen
Our team’s previous meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of closed-loop insulin system (CLS) in non-pregnant individuals with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). In this study, we aim to discuss the broader application of CLS in a more diverse population and address the current challenges and future development directions.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p11-14 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.4.055
Recommended Articles
Risks and Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy in Children and Young People with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is associated with microvascular and macrovascular complications.Duration of diabetes, poor glycaemic control, high blood pressure and proteinuria are reported risk factors contributing to the development of diabetes related complications.
Short Commentary on African Cuisine-Centered Insulin Therapy: Expert Opinion on the Management of Hyperglycaemia in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
The traditional African diet is considered a very rich source of nutrition being largely whole with minimal processing [1]. There are unique challenges when managing Diabetes in Africa especially when making nutritional recommendations. An appropriate diet protects organ (heart, liver, pancreas etc.) health and vice versa.
Elevated Opioid Growth Factor Alters the Limbus in Type 1 Diabetic Rats
Ocular surface complications occur in more than 50% of individuals diagnosed with diabetes. The financial and health-related burden of diabetes is increasing annually. Several major ocular complications associated with diabetes involve the limbus. The vascular limbus, adjacent to the avascular cornea, is the source of circulating growth factors, elevated glucose, and cytokines for the cornea.
Type 1 Diabetes: A Disorder of the Exocrine and Endocrine Pancreas
Type 1 diabetes has historically been described as an endocrine (β-cell) specific autoimmune disease. However, a substantial reduction (20-50%) in pancreas organ size and subclinical to symptomatic exocrine pancreatic insufficiency are present at diagnosis and may begin even prior to the development of islet autoimmunity. The mechanisms of exocrine loss in type 1 diabetes are not well understood, but leading hypotheses include developmental defects, β-cell loss resulting in exocrine atrophy, or autoimmune or inflammatory destruction of exocrine cells.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
