Loading
Journal of Cellular Signaling
ISSN: 2692-0638
Latest Articles
PAX-Interacting Protein 1 (PTIP) Promotes Apoptosis
Ching-Jung Huang , Hyein Cho , Chuan Li , Kangsan Kim , Danyang Yu , Daechan Park , Y. Jessie Zhang , Haley O. Tucker
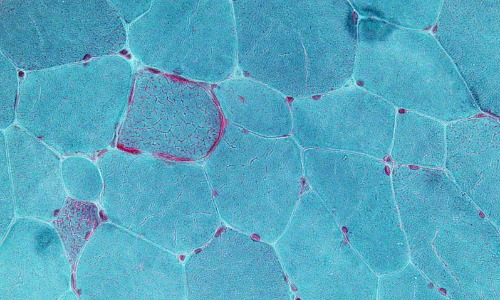
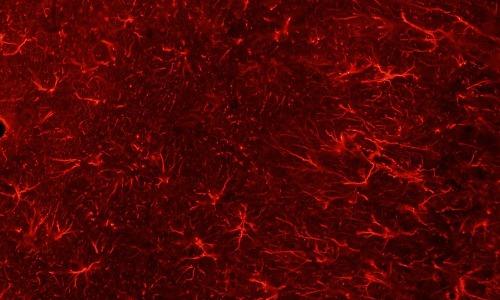
PAX-interacting protein 1 (PTIP/PAXIP1) was discovered and initially characterized over three decades ago as a 1,056 amino acid-containing protein with six tandem BReast cancer C-Terminal (BRCT) repeats. PTIP functions broadly to catalyze histone methylation in DNA damage repair and within the hematopoietic lineage, to promote immunoglobulin variable region (variable, diversity, joining [VDJ]) and class switch recombination (CSR).
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 4, p126-141 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.142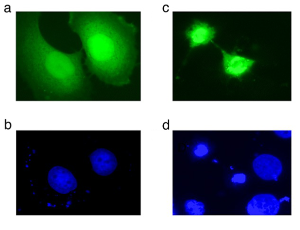
A Newly Characterized, Two BRCT Domain-Containing Isoform of PAX-Interacting Protein (PTIP) Generated via Frame Shift and Alternative Pre-mRNA Splicing
Ching-Jung Huang , Chuan Li , Danyang Yu , Hyein Cho , Kangsan Kim , Y. Jessie Zhang , Daechan Park , Haley O. Tucker
In an effort to clone polyglutamine-rich factors from activated B lymphocytes of mice, we discovered and describe here a previously uncharacterized isoform of PTIP/PAXIP1. By virtue of a two-nucleotide frameshift followed by alternative pre-mRNA splicing, this shorter isoform of 576 amino acids (termed PTIP576) retained only the two central BRCT domains of previously characterized PTIP and encodes a unique and structurally disordered 50 residue C-terminus.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 4, p142-155 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.143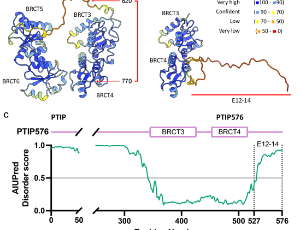
Pathogenic Pathways and Therapeutic Strategies in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD)
Kenley M. Preval , Abigail O. Smith , Gregory J. Pazour
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is the most common inherited kidney disorder and a major cause of end-stage renal disease. The disorder is primarily caused by pathogenic variants in PKD1 or PKD2, which encode the ciliary proteins polycystin-1 and polycystin-2. Loss of polycystin function disrupts calcium and cAMP signaling within the primary cilium, altering epithelial proliferation and fluid secretion that drive cyst formation and progressive kidney enlargement.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 4, p156-169 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.144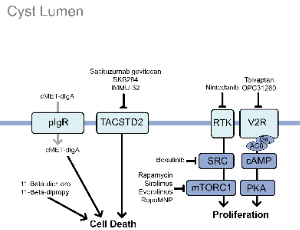
When Cells Speak in Many Languages: The Evolving Story of Cellular Signaling
Vivek K Pandey
The current issue of the Journal of Cellular Signaling brings together a diverse set of studies that collectively broaden our understanding of cellular communication, from canonical biochemical pathways to emergent bioelectric and metabolic signaling systems. This editorial review synthesizes the major findings and conceptual advances presented in Volume 6 Issue 3, highlighting the converging trends that redefine how we view signaling as an integrative, dynamic, and multi-dimensional process.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 4, p178-180 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.146
Ubiquitination of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors and Associated Synaptic Proteins In Vitro and In Vivo
Li-Min Mao , John Q. Wang
Metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptors are a family of G protein-coupled receptors. These receptors are widely distributed in the brain and are critical for the modulation of synaptic transmission and plasticity. Emerging evidence shows that mGlu receptors themselves are subject to a dynamic posttranslational modification involving protein ubiquitination.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 4, p170-177 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.145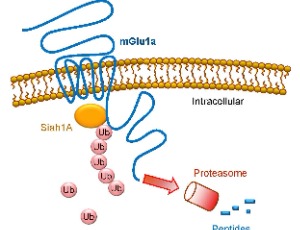
Trending Special Issues
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.