Loading
Journal of Cellular Immunology
ISSN: 2689-2812
Latest Articles
18F-FDG PET/CT in the Diagnostic Workup of Fever and Inflammatory Syndromes of Unknown Origin in the Elderly: A Valuable Tool with a Need for Clinical Finesse
Emmanuel Andres , Alessio Imperiale , Thierry Lavigne , Noel Lorenzo Villalba
Fever and inflammatory syndromes of unknown origin (FUO and IUO) represent some of the most challenging diagnostic entities in clinical medicine. These conditions often trigger extensive investigations, prolonged hospitalizations, and sometimes empirical treatments with limited benefit. The diagnostic complexity is even greater in the elderly, where clinical presentations are frequently atypical, underlying conditions are numerous, and physiological responses to illness are blunted or masked.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 5, p185-187 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.238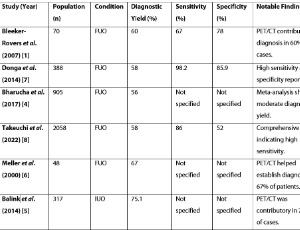
Revisiting Vaccine Innovation: A Critique of the “Generation Gold Standard” Initiative
Yongxin Zhang
The “Generation Gold Standard” (GGS) initiative, announced by NIH and BARDA, aims to develop universal vaccines for influenza and coronaviruses using β-propiolactone (BPL)–inactivated whole-virus technology. This approach, historically used in vaccines like Sinovac’s CoronaVac, is praised for its scalability but has faced scrutiny for limited durability and cross-protection. As the world seeks robust pandemic preparedness post-COVID-19, GGS’s reliance on an established platform raises questions about its transformative potential.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 5, p188-191 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.239
A Commentary on USP50 and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation: Revisiting Experimental Rigor with ASC-Deficient RAW264.7 Cells
Jing-Rong Liang , Jie Guo , Feng-Yi Mai , Ai-Guo Xue , Chen-Guang Li
The recent study by Zhao et al. in Frontiers in Immunology reported that bile acids induce USP50 expression in macrophages, which then deubiquitinates ASC to promote NLRP3 inflammasome activation and HMGB1 release, ultimately driving gastric cancer progression through PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways. These findings provide valuable insights into the potential role of bile reflux-driven inflammation in the pathogenesis of gastric cancer. In general, this is an insightful piece of research.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 5, p192-196 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.240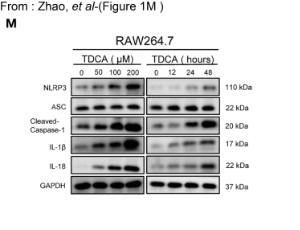
HMGB3: A Potential Immunotherapeutic Target in Glioblastoma Multiforme—Current Strengths, Existing Limitations, and Future Perspectives
Xing-Long Li , Feng-Yi Mai , Xin-Yu Li , Jie Guo , Chen-Guang Li
A key strength of Wang et al.’s study lies in its rigorous integration of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and bulk RNA-seq, which overcomes the inherent limitations of each technology alone. ScRNA-seq dissects GBM cellular heterogeneity to identify 21 cell clusters and 1,150 cell-type-specific markers, while bulk RNA-seq captures transcriptomic patterns across large cohorts.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 5, p181-184 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.237
Diversity and Evolutionary Adaptations of the IMD Signaling Pathway in Hemipteran Innate Immunity against Bacterial Infections
Mario Henry Rodríguez , Eduardo Daniel Rodriguez-Aguilar
Insects conform large numbers of parasites and pathogens in diverse habitats. Cuticular structures on their body surfaces and secreted membranes in their digestive tracts are the first defensive barriers to prevent entry of invading organisms. Across the extended range of genera and species, insects acquired common first front defensive mechanisms.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 5, p197-203 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.241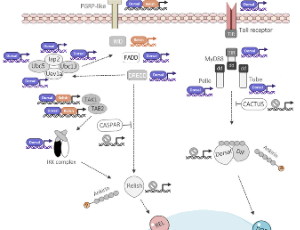
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
