Loading
Journal of Cancer Immunology
ISSN: 2689-968X
Latest Articles
Should You Be Afraid of the Big Bad Wolf? A Practical Real-world Review for the Comfortable Use of Bosutinib in the Therapy of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Jeffrey H Lipton
Bosutinib is a second generation (2G) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) for the therapy of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). It is effective, as other 2g TKIs and long term, is likely the safest, with few significant issues. Short term adverse events which have inhibited their use in the past can be overcome with some simple maneuvers which will be reviewed here. The background for bosutinib, patient selection, and a process for successfully starting patients on therapy will be outlined.
J Cancer Immunol, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 4, p166-173 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.7.115
Highlighting the Role of DCLK1 in Tumor Invasion and Potential for Therapeutic Intervention
Molly E. Muehlebach , Sufi Mary Thomas
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) accounts for nearly 5% of global cancer deaths per year, with epidemiological studies suggesting an expected 30% increase in cases by 2030 due to rising incidence of viral infection (i.e. huma papilloma virus [HPV]). Treatment consists primarily of surgical tumor removal accompanied by post-operative chemoradiation therapy; however, disease recurrence is still an issue amongst 10–26% of patients. Doublecortin-like kinase 1 (DCLK1) is a microtubule-associated protein with dual kinase activity, and upregulation has been associated with poor prognosis in multiple solid tumors.
J Cancer Immunol, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 4, p174-180 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.7.116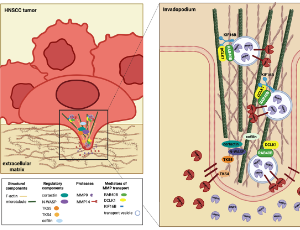
Re-engineering the Tumor–Immune Interface—Emerging Frontiers in Cancer Immunology and Immunotherapy
Sanjay K. Srivastava
Cancer immunology continues to redefine the landscape of oncology, shifting the therapeutic paradigm from direct cytotoxicity toward immune modulation and re-education. The latest publications in the Journal of Cancer Immunology capture this evolution with remarkable clarity—highlighting how manipulating both the tumor microenvironment (TME) and the immune effector landscape can unlock durable anti-tumor immunity
J Cancer Immunol, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 4, p181-182 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.7.117
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.