Loading
Archives of Proteomics and Bioinformatics
ISSN: 2767-391X
Most Read Articles
In silico Analysis for the Repurposing of Broad-spectrum Antiviral Drugs against Multiple Targets from SARS-CoV-2: A Molecular Docking and ADMET Approach
Arpana Parihar , Tabassum Zafar , Rekha Khandia , Dipesh Singh Parihar , Rupali Dhote , Yogesh Mishra , Raju Khan
SARS-CoV-2 belongs to the genus Beta of the Coronaviridae family of enveloped single-stranded, positive-sense ribonucleic acid (RNA) with a genome length of 30,000bp. The virion is composed of various non-structural (RNA dependent RNA polymerase also known as RdRp) and structural proteins such as Spike (S), Nucleocapsid (N), Matrix (M), and Envelope (E) proteins.
Arch Proteom and Bioinform, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 1, p3-14 | DOI: 10.33696/Proteomics.3.012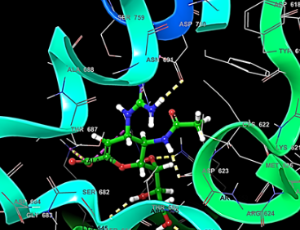
Antisense Inhibition of accA in E. coli Suppressed luxS Expression and Increased Antibiotic Susceptibility
Tatiana Hillman
Multidrug resistant (MDR) bacteria, which are resistant to more than one antibiotic, present an enormous challenge for medical communities and organizations worldwide. For example, Acinetobacter baumannii is a highly contagious MDR gram-negative bacterium (GNB) that inhabits hospitals and causes 64% of urinary tract infections associated with the use of catheters. Alexopoulou et al. found that there were more healthcare-associated infections caused by GNB than Gram-positive Cocci (GPC) bacte
Arch Proteom and Bioinform, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p4-19 | DOI: 10.33696/Proteomics.2.007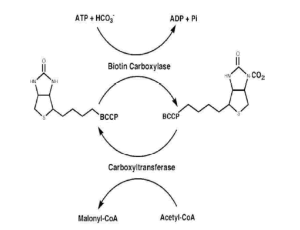
Comment on “Systematic Identification and Analysis of Light-responsive Circular RNA and Coexpression Networks in Lettuce (Lactuca sativa)”
Zhao Yang , Yongjun Wu
Light is one of the most important environmental factors that affect plant growth and development, and it is also the main energy source for plants and other living things. Plants use light to assimilate inorganic matter into organic matter through photosynthesis and store them in the form of chemical energy. As an environmental signal, light mediates the
Arch Proteom and Bioinform, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p9-12 | DOI: 10.33696/Proteomics.1.002
Identification of the Molecular Basis of Anti-fibrotic Effects of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Activator Using the Human Lung Fibroblast
Sunhwa Kim , Ashmita Saigal , Weilong Zhao , Peyvand Amini , Alex M. Tamburino , Subharekha Raghavan , Maarten Hoek
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is an irreversible fibrotic lung disease with unknown etiology [1-3]. Although two approved medications, pirfenidone and nintedanib, are able to slow down lung function decline in IPF patients, many other chronic pathologic conditions such as dyspnea and pulmonary hypertension (PH) and overall disease progression,
Arch Proteom and Bioinform, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p13-30 | DOI: 10.33696/Proteomics.1.003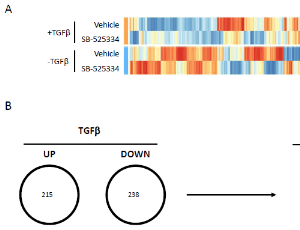
Ramifications of the Diverse mRNA Patterns in Acanthamoeba royreba
Richard Tyndall , Ibne Ali , Anthony Newsome
Acanthamoeba was first described by Castellani and represents single-cell eukaryotes existing as either cellular trophozoites (25–40 ?m) or under adverse conditions (desiccation, lack of food, and extreme pH or temperature fluctuations), as dormant cysts (13–20 ?m). The cysts are known to be resistant to antibiotics, the effects of chlorine, and very low temperatures, and have been shown to maintain viability for over 20 years.
Arch Proteom and Bioinform, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p38-46 | DOI: 10.33696/Proteomics.1.005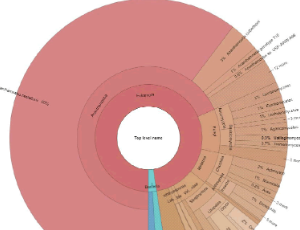
LINE-1 Retrotransposon-derived Proteins: The ORFull Truth?
Vuong, L.M , Donovan, P.J.
In the last few decades there has been a growing interest in the role of transposable elements (TEs), colloquially referred to as “jumping genes” in human biology [1-4]. TEs, and a specific subset of this clade, retrotransposons, are widespread throughout eukaryote genomes. The socalled long interspersed elements-1 (LINE-1 or L1) are of especial interest because they represent the only class of retrotransposons in the human genome that are fully autonomous,
Arch Proteom and Bioinform, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p47-55 | DOI: 10.33696/Proteomics.2.010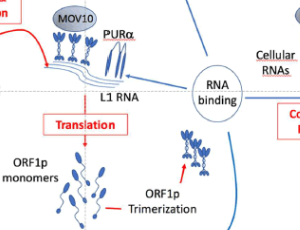
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
