Loading
Archives of Nephrology and Renal Studies
ISSN: 2771-1889
Featured Articles
The RiVUR Study Outcomes and Implications on the Management of Vesicoureteral Reflux
Tiffany Damm, Ranjiv Mathews
The Randomized intervention for Vesicoureteral Reflux (RiVUR) study was an effort by the National Institute of Health to identify the most significant question on the management of vesicoureteral reflux (VUR), i.e. Did antibiotic prophylaxis reduce the incidence of recurrent urinary tract infections (UTI) in children with VUR? During the initial phases of the RiVUR study, several similar studies were performed that seemed to indicate lack of benefit of antibiotic prophylaxis in VUR.
Arch Nephrol Ren Stud, 2022, Volume 2, Issue 1, p1-5 | DOI: 10.33696/nephrology.2.006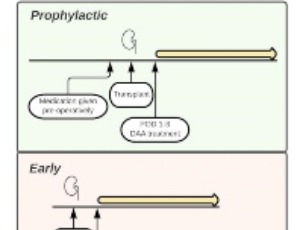
A Case Report and Literature Review on Complications of Pediatric Maintenance Intravenous Fluids
Jaicy Pottokaran, Larry T Patterson, Mark S Segal
After establishing the new standard of care of isotonic fluids for maintenance therapy, there has not been a systematic follow-up to determine whether the goal of the switch has been achieved or whether there have been any unexpected complications with the change. This is a brief review of the history of maintenance intravenous fluids and potential complications of isotonic fluid therapy spurred by a case.
Arch Nephrol Ren Stud, 2024, Volume 4, Issue 1, p1-7 | DOI: 10.33696/nephrology.4.010
Peritoneal Imaging may be the Last Piece of the Puzzle for Precision Evaluation of Peritoneal Function
Xiangwen Diao, Xiao Yang
Due to changes in end-stage renal disease (ESRD) policies in many countries and the impact of COVID-19, the importance and demand for peritoneal dialysis (PD) as a home dialysis treatment modality is growing prominently [1]. However, peritoneal membrane dysfunction remains a bottleneck restricting the application of PD. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop new methods to accurately assess peritoneal function.
Arch Nephrol Ren Stud, 2022, Volume 2, Issue 1, p6-8 | DOI: 10.33696/nephrology.2.007
Review of Renal Transplantation of Hepatitis C Viremic Donor Organs into Aviremic Recipients
Jiawei Cui, Roman Perri
The development of direct-acting antiviral agents for the treatment of Hepatitis C (HCV) has changed the practice of treating patients with HCV. In particular, organ transplant recipients who have not previously been exposed to HCV are now able to consider receiving an organ from a donor who is infected with HCV, and anticipate effective antiviral therapy after transplantation.
Arch Nephrol Ren Stud, 2022, Volume 2, Issue 1, p9-16 | DOI: 10.33696/nephrology.2.008
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
