Loading
Archives of Cancer Biology and Therapy
ISSN: 2692-8302
Most Read Articles
Uniportal VATS Lobectomy for Lung Cancer: Feasibility and Cost Effectiveness in a Single Center Experience
Crucitti Pierfilippo , Longo Filippo , Tacchi Giovanni , Manca Paolo , Frasca Luca , Carannante Filippo , Spoto Silvia , Citarella Fabrizio , Tonini Giuseppe
In last decades, video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) together with robotic-assisted thoracic surgery (RATS) can be considered the biggest innovation in thoracic surgery. This approach drastically changed the way of performing surgical operations, improving patient’s outcome undergoing thoracic surgery.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p1-10 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.1.001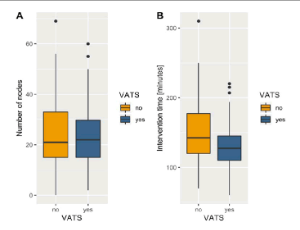
Forces, Chromosomal Configurations, and Carcinogenesis: Towards Another Therapeutic Approach
Michael M. Lieber
Previous studies of in vitro and in vivo morphogenesis may suggest a more inclusive principle governing biological processes. In this regard, methylglyoxal (MG) in very low, non-toxic concentrations and ascorbic acid have been shown to promote in vitro morphogenesis in various types of plants. Forces of cohesion and adhesion might be involved in such development. These are conveyed through the electronic desaturation of protein by means of MG and ascorbic acid.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p1-7 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.2.016
Impact of Cisplatin Dosing Regimens on Mammary Tumor Growth in an Animal Model
James A. Koziol , Theresa J. Falls , Jan E. Schnitzer
In a recent paper, we introduced a variant of the classical Simeoni tumor growth model, and illustrated its value in assessing tumor growth in a reproducible mouse model for mammary tumors. Our modification consisted of incorporating delay differential equations in the mathematical formulation of the Simeoni model, to represent the delay in drug action often observed under chemotherapeutic or immunotherapeutic regimens.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p18-21 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.1.004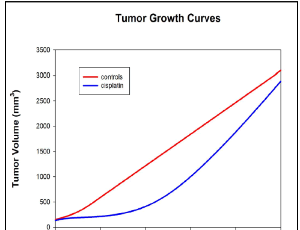
VA-Radiation Oncology Quality Surveillance Program: Enhancing Quality Measure Data Capture, Measuring Quality Benchmarks and Ensuring Long Term Sustainability of Quality Improvements in Community Care
Evangelia Katsoulakis , Rishabh Kapoor , John Park , Christina Chapman , Abhi Solanki , Lindsay Puckett , Rebecca Hagan , William Sleeman , Jatinder Palta , Michael Hagan
Delivery of high-quality cancer care improves oncologic outcomes, including survival and quality of life. The VA National Radiation Oncology (NROP) established the VA Radiation Oncology Quality Surveillance Program (VAROQS) which has developed clinical quality measures (QM) as a measure of quality indices in radiation oncology. We sought to measure quality in community care, assess barriers to data capture, and develop solutions to ensure long term sustainability of continuous quality improvement for veterans that receive dual care, both within the VA and in non-VA community care (NVCC).
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 2, p25-30 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.1.006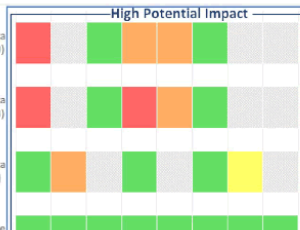
Synthetic Lethal Drug Combinations Targeting Proteasome and Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in TP53-Mutated Cancers
Shaoli Das , Xiang Deng , Kevin Camphause , Uma Shankavaram
Background: We have recently published SL-BioDP, a web resource for querying, exploration and visualization of potential synthetic lethal targets and possible synergistic drug combinations for 18 cancer types. Methods: From our predictive synthetic lethality model used in SL-BioDP, we inferred TP53 mutation lead to potential synergistic drug combination of Bortezomib and Vorinostat. Here we show, how to extrapolate the drug combination results by combining drug screening data from cancer cell lines and showed the potential synergy of the drug targets, proteasome, and histone deacetylase (HDAC) pathways respectively, for patient survival advantage.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 2, p42-47 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.1.009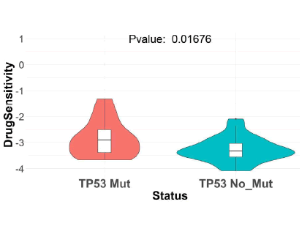
Influence of Clinical Risk Factors on Outcomes in Men with Stage I Non-Seminomatous Germ Cell Tumor Undergoing Robot-Assisted Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection
Dora Jericevic , Jacob Taylor , William C. Huang
We recently published our multi-institutional experience performing primary robot-assisted retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RA-RPLND) for men with non-seminomatous germ cell tumor (NSGCT). We concluded that primary RA-RPLND for NSGCT can be performed safely with low complication rates, acceptable early oncologic outcomes, and lower overall theoretical chemotherapy burden. In this commentary, we explore outcomes in clinical stage I patients stratified by clinical risk factors (RF) and estimate reductions in chemotherapy burden.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p64-67 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.1.014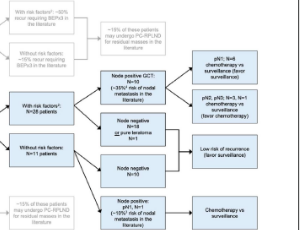
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
