Loading
Archives of Cancer Biology and Therapy
ISSN: 2692-8302
Most Cited Articles
Radical Radiotherapy of Locally Advanced Cervix Uteri Carcinoma
Alparslan Serarslan, Deniz Meydan, Rana Elif Yildiz
External beam radiotherapy with concomitant platinum-based chemotherapy followed by brachytherapy is defined as radical radiotherapy of cervix uteri carcinoma. Radical radiotherapy is the gold standard treatment for locally advanced cervix uteri carcinoma. The rates of survival and treatment-related adverse events in patients with cervix uteri carcinoma are affected by both stage of disease and treatment. Both should be optimal in proportion to the available facilities. Here, recommendations from the current literature are presented.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p8-14 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.2.017
Angioimmunoblastic T cell Lymphoma Microenvironment
Sergiu Pasca, Ancuta Jurj, Daniela Matei
Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL) is one of the most common T-cell lymphomas, second only to peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS). Initially AITL was considered a non-malignant lymphadenopathy with immune hyperactivation, nowadays being classified as a PTCL.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p11-13 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.1.002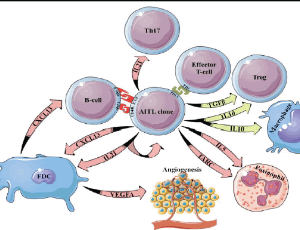
Lessons Learnt from COVID-19: How Can We Prepare for Another Pandemic?
Matthew I. Ehrlich, Muhammad Wasif Saif
Five months into the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S. death toll from the virus has now surpassed 100,000 people. Many more cases remain nationwide, while an unknown number of patients currently harbor the virus asymptomatically. While health officials are now optimistic regarding the decline in prevalence and number of deaths due to COVID-19 and the possibility of a vaccine by the fall, we cannot lose sight of the bigger picture: the next pandemic.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p22-24 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.1.005
VA-Radiation Oncology Quality Surveillance Program: Enhancing Quality Measure Data Capture, Measuring Quality Benchmarks and Ensuring Long Term Sustainability of Quality Improvements in Community Care
Evangelia Katsoulakis, Rishabh Kapoor, John Park, Christina Chapman, Abhi Solanki, Lindsay Puckett, Rebecca Hagan, William Sleeman, Jatinder Palta, Michael Hagan
Delivery of high-quality cancer care improves oncologic outcomes, including survival and quality of life. The VA National Radiation Oncology (NROP) established the VA Radiation Oncology Quality Surveillance Program (VAROQS) which has developed clinical quality measures (QM) as a measure of quality indices in radiation oncology. We sought to measure quality in community care, assess barriers to data capture, and develop solutions to ensure long term sustainability of continuous quality improvement for veterans that receive dual care, both within the VA and in non-VA community care (NVCC).
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 2, p25-30 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.1.006
Exosome to Promote Cancer Progression via Its Bioactive Cargoes
Austin McMasters, Kelly M McMasters, Hongying Hao
Exosomes are nanosized, organelle-like membranous vesicles secreted from various cell types, including normal cells and cancer cells. Exosomes contain abundant bioactive molecules, including nucleic acids, lipids, and proteins and dynamically participate in intercellular communications. By shuttling the functional molecules into the recipient cells, exosomes secreted by cancerous cells can alter the cellular environment to favor tumor growth and metastasis.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p29-34 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.2.021
Reduced BCR Signaling and a Metabolic Shift Accompanies Malignant Progression of Follicular Lymphoma: A Lesson from Transcriptomics
Cesare Sala, Annarosa Arcangeli
In the manuscript entitled “The ion channels and transporters gene expression profile indicates a shift in excitability and metabolisms during malignant progression of Follicular Lymphoma”, we reported recent advances in our understanding of how the gene expression profile of ion channels and transporters (ICT-GEP) contributes to identify specific signatures associated with Follicular Lymphoma (FL), with those FL that acquire chemoresistance after a relapsing-remitting course, and with the more aggressive Diffuse Large Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL), which in some cases represent the evolution of FLs.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 2, p31-36 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.1.007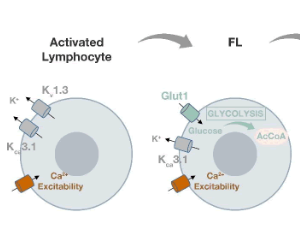
The Challenge of Cognitive Dissonance in the Delivery of Precision Medicine in Veterinary Oncology
J. Cawley, C. Khanna
The use of molecular and genomic analysis of a cancer as a means to define a patient-specific treatment is interchangeably referred to as Precision Medicine, Personalized Medicine, or Genomically-directed medicine (herein, collectively PMED). In the foregoing commentary we have focused on PMED approaches related to treatment selection and do not prioritize the development of novel molecular assays used to guide patient diagnostics or prognostication.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 2, p37-41 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.1.008
Role of the Gut Microbiome in the Modulation of Cancer Immunotherapy Response
Sachin Kumar Deshmukh
The gut microbiome or gut flora is a vast community of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and fungi that inhabit the digestive tract of the human and other animals. In the human body, bacterial species colonize into the oral cavity, skin, vagina, and placenta, however, the largest population of microorganisms resides in the intestine. The majority of gut microbiota belong to the phyla Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p52-54 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.1.011
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
