Loading
The Archives of Psychiatry
ISSN: 2995-8776
Latest Articles
Digital Conversations about Severe Depression Symptoms Across Different Ethnic and Racial Groups: A Big-data, Machine Learning Analysis
Ruby Castilla-Puentes , Silvia Ferrer , Ariceli Alfaro , Laura Jimenez-Parrado , Whitney S. Cordoba-Grueso , Sebastian Castilla
Depression is a common but serious mental disease that ranges widely in severity. It affects 5% of adults worldwide, and approximately 280 million people in the world suffer from the condition. The National Center for Health Statistics reported in 2019 that 2.8% of adults had symptoms of severe depression, 4.2% had moderate depression, and 11.5% had mild depression, in the two weeks recorded. One way to early detect symptoms of depression is to analyze what people are talking about - their conversations.
Arch Psychiatry, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p1-11 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.3.019
Listening In: A Model of Healing Rooted in Developmental Science
Claudia M. Gold
Practitioners working on the front lines with young children may feel pressure to advise, instruct, and intervene. Decades of research in contemporary developmental science point to an alternative approach termed “listening in.” This commentary will review evidence supporting this approach, showing its application in a common clinical scenario. It will root the approach in concepts of cultural difference and the importance of cultivating a sense of belonging.
Arch Psychiatry, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p12-14 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.3.020
The Challenge of Disentangling Parkinson’s-related Fatigue and Neuropsychiatric Symptoms
Asenath X. A. Huether , Jau-Shin Lou
Fatigue is among the most prevalent and debilitating non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease (PD). In the focal article, “Screening cut-off scores for clinically significant fatigue in early Parkinson’s disease”, we discussed the challenges of evaluating fatigue in PD and proposed cut-off scores for select fatigue assessments. This commentary expands on the challenges of evaluating fatigue, especially when it presents alongside psychiatric symptoms. We examine and compare the similarities of fatigue and depression, anxiety, and apathy.
Arch Psychiatry, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p15-17 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.3.021
Epigenetic Regulation in Alzheimer's Disease – Development, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
Mingyu Ye , Shuying Chen , Yong Lin , Shaomin Li
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) remains a formidable challenge in neuroscience, with its complex pathology still lacking an effective cure. Recent research has highlighted the critical role of epigenetic regulation in AD, demonstrating how environmental factors and genetic predispositions influence disease progression at a molecular level. This commentary examines key advancements in AD-related epigenetic research, with a particular focus on histone deacetylases (HDACs) and adrenergic signaling-two mechanisms that have emerged as promising therapeutic targets for mitigating AD symptoms and slowing neurodegeneration.
Arch Psychiatry, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p21-25 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.3.023
How to Treat Patients with Severe Intellectual Disabilities in Psychiatry?
Michel Bourin
Many adults with intellectual disabilities have serious behavioral problems, sometimes requiring medical intervention. To this end, it is essential to improve the medical care of this population because there is a very large disparity in the care offered to them compared to the general population. Challenging behaviors constitute a real challenge in supporting people with severe intellectual disabilities, which can cause great difficulty for individuals, institutions and psychiatric services.
Arch Psychiatry, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p26-29 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.3.024
Language Disorders in People with Profound Intellectual and Multiple Disabilities
Michel Bourin
People with profound intellectual and multiple disabilities present significant challenges to those who care for them, and those who commission and manage the services they receive. Childhood disabilities are a cause of major concern causing significant handicap to the affected children. At least one in ten children are born with or acquire a physical, mental or sensory impairment.
Arch Psychiatry, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p30-34 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.3.025
Diagnosis and Assessment of Non-Suicidal Self-Injury in the Background of Integrated Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine
Jin Weidong , Honghui Wei , Haihan Chen , Xin Ren , Sun Fengli
Non-suicidal self-injury (NSSI) refers to deliberate and repeated acts of damaging one's own body tissue without suicidal intent. It is usually related to depression, bipolar disorder (BD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and borderline personality disorder (BPD). Integrated Chinese and Western medicine treatment is one of the effective methods for the treatment of NSSTI at present.
Arch Psychiatry, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p35-39 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.3.026
The Relationship between Physical Activity Level and Short Video Addiction in Individuals with Bipolar Disorder
Neslihan Lök , Sefa Lök , Fatih Sarısoy
The aim of this study is to investigate the relationship between physical activity level and short video addiction in individuals diagnosed with bipolar disorder. This study was planned as a descriptive relational study. The sample of the study consisted of 100 individuals over the age of 18 with bipolar disorder who were followed up in a family health center in Selçuklu district of Konya province. The data of the study was collected by face-to-face interview method.
Arch Psychiatry, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p40-45 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.3.027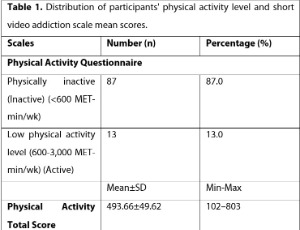
Therapeutic Alliance and Affordability: Indicators of Early Dropout in Telepsychiatry
Jonika Tannous , Georgia Gaveras , Cheryl Person
Early dropout from psychiatric care remains a persistent barrier to effective treatment. To investigate the role of therapeutic alliance and financial burden in contemporary treatment settings, we conducted a retrospective analysis using data from a large national telepsychiatry platform. The study included 796 adults (≥18 years) who completed at least two visits and had working alliance inventory-short revised (WAI-SR) scores within 45 days of their initial appointment.
Arch Psychiatry, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p46-55 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.3.028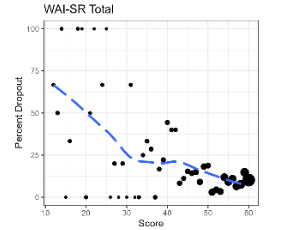
Borderline Personality Disorder: A Valid Psychiatric Diagnosis
Mark L. Ruffalo
The validity of borderline personality disorder (BPD) has become an urgent issue in psychiatric nosology, with some proposing its absorption into complex posttraumatic stress disorder and others questioning its utility due to stigma. With planning for DSM-6 underway, reassessing the validity of BPD is both timely and necessary.
Arch Psychiatry, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p61-63 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.3.030
Pain in People with Profound Intellectual and Multiple Disabilities
Michel Bourin , Patrice Absil
The inability to communicate verbally does not in any way negate the possibility that an individual may be experiencing pain and may need appropriate treatment to relieve their pain. Pain can be expressed differently from one person to another. It can be difficult to decode and interpret and, as a result, can be underestimated by caregivers, particularly in people with multiple disabilities, due to their sensory specificities and unique communication modalities.
Arch Psychiatry, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p61-71 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.3.031
Two Brief Communications on Autism: The Relationship Between Testosterone and Stem Savants and an Ethological View of Repetitive Behavior
Michele Di Salvo
This commentary addresses two distinct aspects of autism spectrum condition. First, it critiques the proposed link between fetal testosterone levels and the emergence of autistic traits, arguing that such theories are reductive and risk overshadowing the profound heterogeneity and individuality of autistic people. The author suggests a more limited, theoretical connection between testosterone-driven neural development and a higher incidence of STEM savant skills in some autistic individuals.
Arch Psychiatry, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p72-74 | DOI: 10.33696/Psychiatry.3.032
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
