Loading
Archives of Cancer Biology and Therapy
ISSN: 2692-8302
2020
Volume 1, Issue 2, p25-51
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
VA-Radiation Oncology Quality Surveillance Program: Enhancing Quality Measure Data Capture, Measuring Quality Benchmarks and Ensuring Long Term Sustainability of Quality Improvements in Community Care
Evangelia Katsoulakis, Rishabh Kapoor, John Park, Christina Chapman, Abhi Solanki, Lindsay Puckett, Rebecca Hagan, William Sleeman, Jatinder Palta, Michael Hagan
High quality cancer care improves patient survival and quality of life. Radiation plays an important role in cancer management, given that over 50% of all cancer patients receive radiation therapy as either a primary treatment or for palliation. Ensuring quality of radiotherapy specifically, is therefore important to achieving optimal patient outcomes.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 2, p25-30 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.1.006
Reduced BCR Signaling and a Metabolic Shift Accompanies Malignant Progression of Follicular Lymphoma: A Lesson from Transcriptomics
Cesare Sala, Annarosa Arcangeli
Lymphoma represents the most common form of hematological malignancy in the developed world, accounting for 3.6% of all cancers and 55.6% of all blood cancers in Europe, with non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL) representing 90% of cases.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 2, p31-36 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.1.007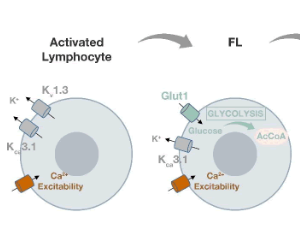
The Challenge of Cognitive Dissonance in the Delivery of Precision Medicine in Veterinary Oncology
J. Cawley, C. Khanna
The use of molecular and genomic analysis of a cancer as a means to define a patient-specific treatment is interchangeably referred to as Precision Medicine, Personalized Medicine, or Genomically-directed medicine (herein, collectively PMED).
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 2, p37-41 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.1.008
Synthetic Lethal Drug Combinations Targeting Proteasome and Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in TP53-Mutated Cancers
Shaoli Das, Xiang Deng, Kevin Camphause, Uma Shankavaram
Tumors harboring mutations in certain oncogenes are often dependent on activation of certain pathways which becomes essential for the survival of the cancer cells. This condition is formally known as synthetic lethality, a state when simultaneous loss of two genes is lethal to a cancer cell, while the loss of the individual genes is not.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 2, p42-47 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.1.009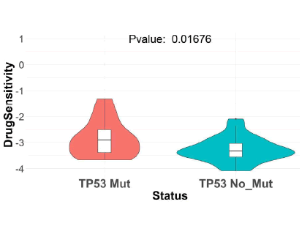
Prognosis and Survival of Medullary Carcinoma of the Breast
Alberto Piamo Morales, García Rojas Mayra
Medullary breast carcinoma (MBC) is a rare tumor, representing 3% to 5% of invasive breast carcinomas. The World Health Organization defines it as a well-circumscribed invasive tumor, composed of poorly differentiated cells, arranged in sheets, without gland formation and a scarce collagen stroma with the presence of a very prominent lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 2, p48-51 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.1.010
Recommended Articles
Ubiquitin Proteasome System Regulates Biological Particles Interaction in Particle Disease (PD) via NF-κB Signaling
Considering their outstanding mechanical character, it is inevitable to utilize titanium and titanium composite for biomedical engineering application [1-6]. However, the particles releasing from these bulks or composites of biomaterials after long term implanting in human body will cause cell apoptosis or cell death, inflammation, bone
Synthetic Lethal Drug Combinations Targeting Proteasome and Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in TP53-Mutated Cancers
Tumors harboring mutations in certain oncogenes are often dependent on activation of certain pathways which becomes essential for the survival of the cancer cells. This condition is formally known as synthetic lethality, a state when simultaneous loss of two genes is lethal to a cancer cell, while the loss of the individual genes is not.
Profiling Proteasome Activities in Peripheral Blood – A Novel Biomarker Approach
The proteasome system in the cell degrades the majority of intracellular proteins. The broad nature of its substrates makes proteasome activity crucial for many cellular functions, such as protein quality control, transcription, apoptosis, immune responses, cell signaling and differentiation. The proteasome system is thus an effective therapeutic target for malignant and non-malignant diseases. In this mini-review, we would like to highlight that proteasome function has also the potential to serve as a biomarker for disease severity and response to treatment. This notion is based on the observation that the six catalytic sites of the proteasome are distinctly altered in peripheral immune cells of patients with chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
