Loading
Archives of Proteomics and Bioinformatics
ISSN: 2767-391X
Latest Articles
Assessing Different Diagnoses in MIMIC-IV v2.2 and MIMIC-IV-ED Datasets
Muhammad Adib Uz Zaman
This study aims to reveal some important insights into the different diagnoses that are listed in Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC) dataset. This dataset includes patients from diverse backgrounds, ethnicity, demographics, etc. The diagnosis records are stored electronically using ICD-09 and ICD-10 codes. It is found that most of the patients were diagnosed at least once for essential hypertension and other related diseases.
Arch Proteom and Bioinform, 2024, Volume 4, Issue 1, p1-5 | DOI: 10.33696/Proteomics.4.014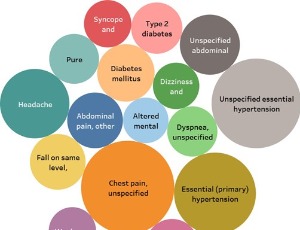
Identifying Biomarkers for Rheumatoid Arthritis and Spondyloarthritis by Machine Learning
Hanson Wen
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and Spondyloarthritis (SpA) are chronic inflammatory diseases characterized by joint inflammation and varying degrees of systemic involvement. RA primarily affects the synovium, often leading to joint destruction and severe disability, while SpA includes diseases such as ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis, impacting both axial and peripheral joints [1].
Arch Proteom and Bioinform, 2024, Volume 4, Issue 1, p6-23 | DOI: 10.33696/Proteomics.4.015
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
