Loading
Archives of Gastroenterology Research
ISSN: 2692-5427
2020
Volume 1, Issue 3, p52-88
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
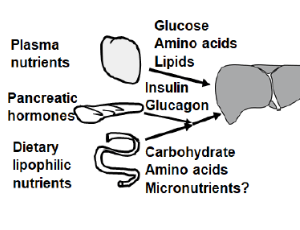
The Link of Nutrient Fluxes to Hepatic Insulin Resistance at Gene Expression
Yan Zhang, Guoxun Chen
Insulin resistance has been studied extensively at systemic, organ, tissue and cellular and molecular levels. Overnutrition plays an essential role in the development of chronic metabolic diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. For subjects without genetic defects, the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes is a graduate process. How the transition from an insulinsensitive state to an insulin-resistant state occurs, and what the roles of nutrients are in the process have not been fully understood. Here, we try to summarize the current understanding of insulin-regulate gene expression in the liver, and describe a phenomenon of hepatic insulin resistance at gene expression (HIRAGE), which may be linked to overnutrition.
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p52-60 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.1.011
Intestinal Barrier Function – a Novel Target to modulate Diet-induced Metabolic Diseases
Siddhartha S Ghosh, Shobha Ghosh
High fat high cholesterol containing Western-type diet (WD)-induced obesity remains one of the major causes for the development of metabolic syndrome and associated metabolic diseases such as Type 2 Diabetes (T2DM) and atherosclerosis (that leads to cardiovascular diseases including heart disease and stroke). In addition to changes in lipid metabolism and excessive lipid accumulation, recent studies have also described direct effects of WD on gut microbiome and attributed dysbiosis of gut flora to the observed metabolic effects.
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p61-65 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.1.012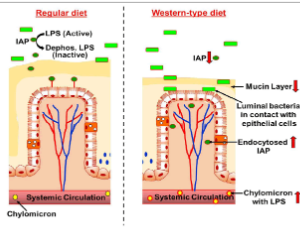
The Consideration of Endometriosis in Women with Persistent Gastrointestinal Symptoms and a Novel Neuromusculoskeletal Treatment Approach
Allyson Augusta Shrikhande
Endometriosis is a chronic, hormone-dependent, inflammatory disease, characterized by the presence and growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterine cavity and it is associated with chronic pelvic pain and infertility. Worldwide, approximately 176 million women between the ages of 15 and 49 are affected by endometriosis. Endometriosis is a complex disease that induces a chronic inflammatory process and can be challenging to treat. Chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS) is defined as pelvic pain lasting greater than three to six months that is not solely related to menstruation, sexual activity or bowel movements.
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p66-72 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.1.013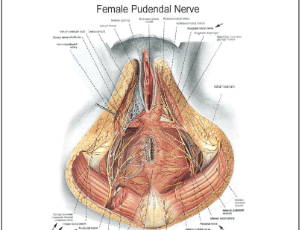
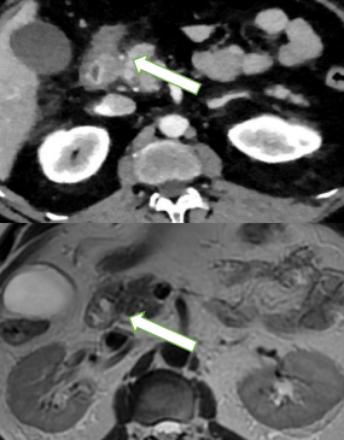
Paraduodenal Pancreatitis: Many faces of the Same Diagnostic Challenge
Giovanni Valentini, Monica Surace, Silvia Grosso, Annalisa Vernetto, Anna Maria Serra, Immacolata Andria, Dario Mazzucco
The term paraduodenal pancreatitis and groove pancreatitis are today used interchangeably, with all conditions having similar manifestations; they refer to an uncommon and still under-recognized form of recurrent or chronic pancreatitis that affects the so-called groove. The groove represents the potential space between the head of the pancreas, medially and the second part of the duodenum, laterally. It is bordered by the duodenal bulb and the third part of the duodenum in the superior and posteroinferior aspects, respectively. The inferior vena cava also forms the posterior aspect. Distal common bile duct (CBD), ampulla, major and minor papilla, superior pancreaticoduodenal vessels and lymphatics, as well as some lymph nodes, are anatomically present in the groove.
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p73-82 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.1.014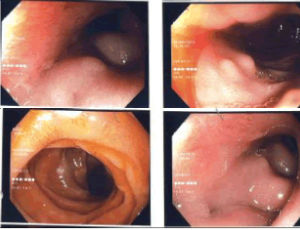
Pharmacologic Therapy with Niacin for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Emerging Evidence
Moti L. Kashyap, Shobha Ganji, Vaijinath S. Kamanna
In pharmacologic doses niacin (nicotinic acid) has been used clinically for over six decades for atherogenic dyslipidemia and reduction of cardiovascular event risk. In combination with statin therapy, it effects regression of coronary atherosclerosis. Emerging evidence indicates a new potential use for niacin for the treatment of NAFLD and its complications. Despite this enormous amount of data on niacin, there is confusion and misconceptions about its use of a drug rather than as a vitamin, its formulations, and how it can be used in clinical practice. The purpose of this invited brief communication is to update and summarize this emerging evidence. We comment on how it may be valuable in the context of other drugs-in-development for NAFLD, especially for combination therapy for synergistic efficacy.
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p83-88 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.1.015
Recommended Articles
The Nature of Radiation-induced Inherited Recessive Gene Mutations in Drosophila Melanogaster
The nature of gene mutations induced by ionizing radiation in germ cells and transmitted to offspring remains one of the most important problems in radiation genetics of higher eukaryotes. The data accumulated in this field were obtained by different authors under different experimental conditions which does not give a complete insight about the nature of radiation-induced inherited mutations at different genome levels (chromosome, gene, DNA).
Karyotypic Profile of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Patients Diagnosed at Tertiary Level in Afghanistan
Balanced translocation resulting in fusion of the Abelson gene (ABL1) from chromosome 9q34 with the breakpoint cluster region (BCR) gene on chromosome 22q11.2 is the pathognomonic molecular driver of CML. The resulting BCRABL 1 fusion gene is both the diagnostic as well as therapeutic target of CML. The first agent with tyrosine kinase inhibitor activity that was licenced in 2000 for treatment of CML patients, was Imatinib, gradually followed by multiple agents with higher efficacy.
Escherichia coli Stress, Multi-cellularity, and the Generation of the Quorum Sensing Peptide EDF
Bacterial communication via quorum sensing (QS) molecules, as well as toxin-antitoxin (TA) gene modules located on bacterial chromosomes are well-studied mechanisms. Escherichia coli mazEF is a stress-induced TA system mediating cell death requiring a QS extracellular death factor (EDF), the pentapeptide NNWNN. MazF is an endoribonuclease specific for ACA sites. During adverse conditions, the activated MazF generates a stress induced translation machinery, composed of MazF-processed mRNAs and selective ribosomes that specifically translate these processed mRNAs.
Constitutively Active Death Receptor Induces Apoptosis in Mammalian Cells
Apoptosis is a physiological response in development and homeostasis of metazoans. Apoptosis is triggered during pathological events as a means to renew affected tissues and eliminate cancer cells. The immune system regulates the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis, where signals such as TNFα or displayed ligands on the surface of immune cells trigger signal cascades by death receptors present on targeted cells.
Commentary on NOBOX Mutations in Premature Ovarian Insufficiency
NOBOX is an ovarian specific transcription factor that plays an important role in follicular growth and survival. Nineteen NOBOX variants have been previously associated with premature ovarian insufficiency (POI). Disease severity in patients with heterozygous and homozygous mutations largely overlap however, hampering genotype-phenotype correlations. We recently reported the first case of biallelic truncating mutations (NM_001080413.3 (NOBOX):c.826C>T, p.(Arg276*) and NM_001080413.3(NOBOX):c.1421del, p.(Gly474Alafs*76)) of NOBOX in two Belgian sisters with POI.
Prevalence of Symptom Clusters in Cancer Patients at First Presentation in Palliative Care Clinic as per Different Disease Groups
Cancer has its own disease burden and patients usually suffer from symptom clusters when they are referred for palliative treatment. Identification of symptom cluster trajectories will help clinician to take into account measures that can optimize quality of life of palliative patients. Therefore the aim of this paper is to determine the overall prevalence of symptoms and symptoms clusters in different disease groups according to etiology at the time of first visit to Palliative care clinic by using HIS Palliative First Assessment note indicating Edmonton symptom scale.
Chimeric Antigen Receptor CAR NK Cells Emerging Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Cancer
Although NK cells are recognized as effector lymphocytes of the innate immune system, they also regulate the adaptive immune response by releasing inflammatory cytokines and developing immunological memory. Unlike other lymphocytes such as T or B cells, NK cells do not express rearrangeable, antigen-specific receptors.
pMB FLASH - Status and Perspectives of Combining Proton Minibeam with FLASH Radiotherapy
Proton minibeam radiotherapy (pMBRT) is an external beam radiotherapy method with reduced side effects by taking advantage of spatial fractionation in the normal tissue. Due to scattering, the delivered small beams widen in the tissue ensuring a homogeneous dose distribution in the tumor. In this review, the physical and biological principles regarding dose distribution and healing effects are explained. In the last decade, several preclinical studies have been conducted addressing normal tissue sparing and tumor control in-vitro and in-vivo, using human skin tissue and mouse or rat models. The major results acquired in these studies are summarized. A further newly emerging therapy method is FLASH radiotherapy, i.e. the treatment using ultra-high dose rates. The possibility of combining these methods in proton minibeam FLASH therapy (pMB FLASH) is worked out. Additionally, technical feasibility and limitations will be discussed by looking at simulations as well as preclinical studies and also pointing out new ways of delivering the desired tumor dose, such as interlacing. We will also highlight the opportunities that emerge regarding high dose radiation, hypofractionation and the combination with immunotherapy.
Flow Cytometric Characterization of Accidental Cell Death Highlights Connections to Regulated Cell Death
Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs) are known by their nature to cause inflammatory responses in numerous disease states from cancer, trauma to age related diseases (e.g. atherosclerosis, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases), these molecules are released by cells undergoing cell death.
Emerging Role of TRPML1 Mucolipin Endolysosomal Channel in Cancer
The transient receptor potential mucolipin 1 (TRPML1) is an endolysosomal channel belonging to the TRP family. Clinically, mutations of TRPML1 have been responsible for a severe lysosomal storage disorder called mucolipidosis type IV.
Manipulating Oxidative Stress Following Ionizing Radiation
It is now well accepted that the ionizing radiation-generated reactive oxygen species (ROS), that constitute ~2/3 of the effects of external beam radiation, do not only produce direct tumor cell death, but also affect the surrounding microenvironment. Moreover, this indirect effect of radiation may result in systemic effects, specifically the initiation of an inflammatory response.
Activation of NLRP3 Inflammosome by N4-Acetyl Cytidine and Its Consequences
N4-acetylcytidine (N4A) is an organic compound and a metabolite of transferrable ribonucleic acid. Its molecular formula is C11H15N3O6. Earlier studies suggest that N4A was mainly found on tRNA and 18S rRNA, while recent studies have shown that there is also a large amount of N4A on mRNA, whose abundance is not even lower than the m7G cap modification carried by mRNA.
Cyclic Nucleotide Signaling Pathways in Apicomplexan Parasites Provide a Valuable Source for Novel Drug Targets
Malaria is one of the most important disabling human, tropical disease caused by different Plasmodium species, which are protozoan parasites belonging to the Apicomplexa. The Apicomplexan parasites have a plastid like structure the “apicoplast” and comprise the genera Plasmodium, Toxoplasma and Cryptosporidium causing malaria, toxoplasmosis, and cryptosporidiosis.
COVID-19 Clinical Research
While the global COVID-19 pandemic has challenged the entire humanity and health systems, it also triggered researchers to urgently perform clinical trials to assess the safety and efficacy of many agents and modalities to combat COVID-19. As of April 22, over 650 clinical studies have been registered both in USA and internationally. Results from these studies are also coming at a brisk pace in this unprecedented emergency.
Ubiquitin Proteasome System Regulates Biological Particles Interaction in Particle Disease (PD) via NF-κB Signaling
Considering their outstanding mechanical character, it is inevitable to utilize titanium and titanium composite for biomedical engineering application [1-6]. However, the particles releasing from these bulks or composites of biomaterials after long term implanting in human body will cause cell apoptosis or cell death, inflammation, bone
Macular Microcirculation after Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment Repair Evaluated by OCT-Angiography
In the process of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD), retinal homeostasis may be adversely affected with resultant modifications in retinal and choroidal tissue. Hypoxia and nutrient deprivation along with inflammation at the detached retina may lead to morphological and microvascularity alterations. These changes imply that the functional status of the macula may not be entirely restored despite anatomical repair.
Therapeutic Values of Ketamine for COVID-19-Cared Patients: An Expert’s Point of View
Ketamine has long been used in the field of anesthesia [1]. Its rapid and long-acting analgesic effects associated with its dissociative properties have also established its use in prehospital and emergency department patients.
Focal Aggregates of Normal or Near Normal Uveal Melanocytes (FANNUMs) in the Choroid. A Practical Clinical Category of Small Ophthalmoscopically Evident Discrete Melanocytic Choroidal Lesions
Multiple types of discrete melanocytic choroidal lesions are currently recognized, including benign choroidal nevi, choroidal malignant melanomas, patches of choroidal melanocytosis, and foci of choroidal melanocytes stimulated paraneoplastically by a systemic nonmelanoma malignant neoplasm.
Uniportal VATS Lobectomy for Lung Cancer: Feasibility and Cost Effectiveness in a Single Center Experience
In last decades, video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) together with robotic-assisted thoracic surgery (RATS) can be considered the biggest innovation in thoracic surgery. This approach drastically changed the way of performing surgical operations, improving patient’s outcome undergoing thoracic surgery.
A Bioinformatics Protocol for Rational Design of Peptide Vaccines and the COVID-19 Rampage
The currently ongoing coronavirus pandemic, the SARSCOV- 2, interchangeably referred to as the COVID-19 infection, has in a short span of time altered the ways and means of almost all of mankind. So strong has been its effect that all human activity ceased in one way or another for a considerable time, led to significant loss of life and economic drain of.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
