Loading
Journal of Cancer Immunology
ISSN: 2689-968X
2019
Volume 1, Issue 1, p24-33
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Prevalence of Symptom Clusters in Cancer Patients at First Presentation in Palliative Care Clinic as per Different Disease Groups
Irum Ghafoor, Haroon Hafeez, Farhat Naz, Muhammad Abubakar, Arif Jamshed
Cancer has its own disease burden and patients usually suffer from symptom clusters when they are referred for palliative treatment. Identification of symptom cluster trajectories will help clinician to take into account measures that can optimize quality of life of palliative patients. Therefore the aim of this paper is to determine the overall prevalence of symptoms and symptoms clusters in different disease groups according to etiology at the time of first visit to Palliative care clinic by using HIS Palliative First Assessment note indicating Edmonton symptom scale.
J Cancer Immunol, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 1 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.1.001
Chimeric Antigen Receptor CAR NK Cells Emerging Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Cancer
Sachin Kumar Deshmukh
Although NK cells are recognized as effector lymphocytes of the innate immune system, they also regulate the adaptive immune response by releasing inflammatory cytokines and developing immunological memory. Unlike other lymphocytes such as T or B cells, NK cells do not express rearrangeable, antigen-specific receptors.
J Cancer Immunol, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 1 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.1.002
pMB FLASH - Status and Perspectives of Combining Proton Minibeam with FLASH Radiotherapy
Judith Reindl, Stefanie Girst
Proton minibeam radiotherapy (pMBRT) is an external beam radiotherapy method with reduced side effects by taking advantage of spatial fractionation in the normal tissue. Due to scattering, the delivered small beams widen in the tissue ensuring a homogeneous dose distribution in the tumor. In this review, the physical and biological principles regarding dose distribution and healing effects are explained. In the last decade, several preclinical studies have been conducted addressing normal tissue sparing and tumor control in-vitro and in-vivo, using human skin tissue and mouse or rat models. The major results acquired in these studies are summarized. A further newly emerging therapy method is FLASH radiotherapy, i.e. the treatment using ultra-high dose rates. The possibility of combining these methods in proton minibeam FLASH therapy (pMB FLASH) is worked out. Additionally, technical feasibility and limitations will be discussed by looking at simulations as well as preclinical studies and also pointing out new ways of delivering the desired tumor dose, such as interlacing. We will also highlight the opportunities that emerge regarding high dose radiation, hypofractionation and the combination with immunotherapy.
J Cancer Immunol, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 1 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.1.003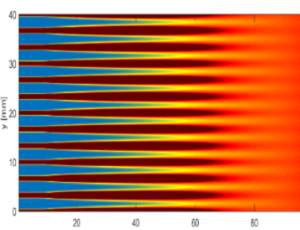
Salivary Protein Antigens for Breast Cancer Biomarkers
Imad Abrao Nemeir, Joseph Saab, Walid Hleihel, Abdelhamid Errachid, Nadia Zine
Breast Cancer is the most regularly diagnosed type of cancer in women in the world, making up on its own 25% of all cases, or nearly 2 million new cases in 2018, and 15% of all cancer related deaths, or around 626,700 deaths for that same year.
J Cancer Immunol, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 1, p24-30 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.1.004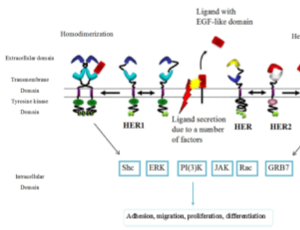
Commentary on "The Gene Master Regulators GMR Approach Provides Legitimate Targets for Personalized, Time-Sensitive Cancer Gene Therapy"
Dumitru Andrei Iacobas
For decades, the scientific community tried hard to identify the gene biomarkers whose mutations or regulations cause (better say are associated with) specific forms of cancer. For instance, the September 17th 2019 release of the Genomic Data Commons Data Portal includes 3,142,246 mutations detected in 22,872 genes sequenced from 37,075 cases of cancers localized in 67 primary sites.
J Cancer Immunol, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 1, p31-33 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.1.005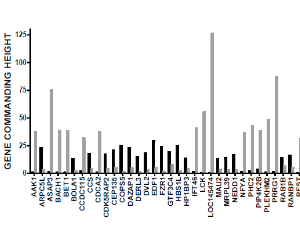
Recommended Articles
Prevalence of Symptom Clusters in Cancer Patients at First Presentation in Palliative Care Clinic as per Different Disease Groups
Cancer has its own disease burden and patients usually suffer from symptom clusters when they are referred for palliative treatment. Identification of symptom cluster trajectories will help clinician to take into account measures that can optimize quality of life of palliative patients. Therefore the aim of this paper is to determine the overall prevalence of symptoms and symptoms clusters in different disease groups according to etiology at the time of first visit to Palliative care clinic by using HIS Palliative First Assessment note indicating Edmonton symptom scale.
Chimeric Antigen Receptor CAR NK Cells Emerging Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Cancer
Although NK cells are recognized as effector lymphocytes of the innate immune system, they also regulate the adaptive immune response by releasing inflammatory cytokines and developing immunological memory. Unlike other lymphocytes such as T or B cells, NK cells do not express rearrangeable, antigen-specific receptors.
pMB FLASH - Status and Perspectives of Combining Proton Minibeam with FLASH Radiotherapy
Proton minibeam radiotherapy (pMBRT) is an external beam radiotherapy method with reduced side effects by taking advantage of spatial fractionation in the normal tissue. Due to scattering, the delivered small beams widen in the tissue ensuring a homogeneous dose distribution in the tumor. In this review, the physical and biological principles regarding dose distribution and healing effects are explained. In the last decade, several preclinical studies have been conducted addressing normal tissue sparing and tumor control in-vitro and in-vivo, using human skin tissue and mouse or rat models. The major results acquired in these studies are summarized. A further newly emerging therapy method is FLASH radiotherapy, i.e. the treatment using ultra-high dose rates. The possibility of combining these methods in proton minibeam FLASH therapy (pMB FLASH) is worked out. Additionally, technical feasibility and limitations will be discussed by looking at simulations as well as preclinical studies and also pointing out new ways of delivering the desired tumor dose, such as interlacing. We will also highlight the opportunities that emerge regarding high dose radiation, hypofractionation and the combination with immunotherapy.
Prospective Evaluation of Effect of Metformin on Activation of AMP-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) and Disease Control in a Sub-group Analysis of Patients with GI Malignancies
Observational studies have demonstrated association of metformin with reduced cancer incidence and mortality in multiple cancer types, including gastrointestinal (GI) malignancies. Anti-neoplastic effects of metformin are believed through many mechanisms including activation of AMP-activated protein kinase, which controls mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) growth regulatory pathway.
Deubiquitinase as Potential Targets for Cancer Immunotherapy
During the last few decades, immunotherapy is considered to be an important approach to help our immune system to fight various kinds of diseases, such as tumor. Sometimes, it works very well for some types of cancers, for example: bladder cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer and lymphoma.
Role of the Gut Microbiome in the Modulation of Cancer Immunotherapy Response
The gut microbiome or gut flora is a vast community of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and fungi that inhabit the digestive tract of the human and other animals [1,2]. In the human body, bacterial species colonize into the oral cavity, skin, vagina, and placenta, however, the largest population of microorganisms resides in the intestine.
Kv1.3 Potassium Channels: Promising Therapeutic Targets in Hematological Malignancies
Voltage-gated Kv1.3 potassium channels control the membrane potential, cellular activation and cell death. Kv1.3 channels have been extensively studied in autoimmune disorders and are promising drug targets for the treatment of solid cancer.
The Safety of High Dose Labetalol in the Pregnant Population
Medical management of hypertension in pregnancy is indicated for severe range blood pressures. This is diagnosed with either systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥ 160 mm Hg and/or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥110 mm Hg on two occasions at least 4 hours apart. When this diagnosis is established, fast-acting anti-hypertensive medications can be utilized for acutely severe range blood pressures.
CTLA-4 and PD-L1 or PD-1 Pathways: Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Cancer Immunotherapy
The immune system developed certain checks and balance to control or inhibit the reactivity against normal cells of the body. Uncontrolled immune responses to the non-self entities such as bacteria, viruses, parasites, or mutated self-antigens can cause an inflammatory reaction and autoimmune diseases.
Cancer Nanomedicine: Strategies to Enhance Tumor Delivery and Immunotherapy
Cancer nanomedicine was originally developed for more efficient delivery of chemotherapeutic agents into tumor, and has been extensively employed as a therapeutic for cancer treatment owing to its unique features in drug delivery, diagnosis and imaging, as well as the therapeutic nature of some nanomaterials themselves.
Targeting "Do Not Eat Me" Signal CD47 in Cancer Immunotherapy
Cells of the innate and adaptive arm of the immune system including macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells, neutrophils, T cells, and B cells, etc. are crucial for the maintenance of the body’s homeostatic balance and prevention of multiple diseases including cancer.
Immunotherapy in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Leukemia is the most common childhood malignancy and is the most common cause of cancer death before the age of 20. Pediatric leukemia can be subdivided into acute versus chronic and lymphoid versus myeloid leukemia.
Small-molecule Interferon Inducers for Cancer Immunotherapy Targeting Non-T cell-inflamed Tumors
Since the discovery of escaping mechanism of tumor from negative immune regulation, the paradigm of drug discovery for anti-cancer agents has been dramatically shifted to cancer immunotherapy (e.g., dendritic cell therapy, CAR-T cell therapy, or antibody therapy) by stimulating patient’s immune system to treat cancer.
Risks and Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy in Children and Young People with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is associated with microvascular and macrovascular complications.Duration of diabetes, poor glycaemic control, high blood pressure and proteinuria are reported risk factors contributing to the development of diabetes related complications.
Cervical Cancer Prevalence in sub-Saharan Africa and HPV Vaccination Policy: A Public Health Grand Challenge?
“Women are not dying because of diseases we cannot treat. They are dying because societies have yet to make the decision that their lives are worth saving.”
Humanized Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T cells
In 1989, researchers proposed an intricate strategy in the field of adoptive cell therapy (ACT). Using the T-cell receptor (TCR) as a template, they replaced the coding sequence for the Vα and Vβ chains with the antigen- recognition domains from an antibody (VH and VL chains).
Gemcitabine in the Era of Cancer Immunotherapy
Gemcitabine is a synthetic pyrimidine nucleoside analogue which is administered intravenously as a chemotherapeutic to treat numerous cancers. Gemcitabine requires transport into cells and activation by phosphorylation, the resulting gemcitabine triphosphate is incorporated into newly synthesized DNA during cell division, inhibiting further DNA synthesis and causing cell death. Gemcitabine is used to treat cancers including those of the pancreas, lung, breast, colon, and ovary either as first or second line treatments as a single agent or in combination.
CART Cells: A New Dawn in Cancer Immunotherapy
Over the last 10 to 15 years the treatment of patients with hematologic malignancies has seen the blossom of a large number of new agents and even new treatment strategies. Monoclonal antibodies (MoAb), TKI inhibitors, checkpoint inhibitors have been introduced in the daily clinical practice and contributed significantly to the improvement of the outcome of hematologic patients. Along with the development of these new drugs, cellular therapies, namely chimeric antigen receptor-engineered T (CART) cells, have revolutionized the therapeutic paradigm of patients with B-cell lymphoid malignancies and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
OGR1-a Novel Modulator Target of Tumor Immunotherapy
Tumors mainly utilize glucose to promote aerobic glycolysis for their survival (Warburg effect). The highly glycolytic environment is not suitable for the survival and function of effector T cells, and leads to the decline of antitumor immunity.
CRISPR Taking the Front Seat in Immunotherapy
CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) technology has dramatically simplified genome editing and is widely applicable in both basic research and therapeutic areas.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.